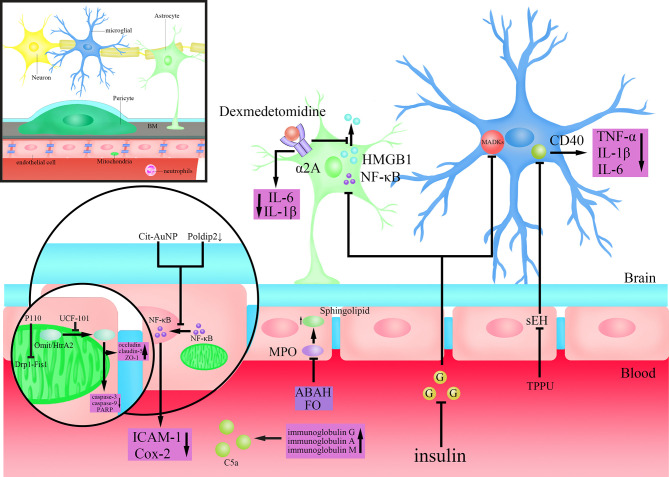
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of action of drugs that may target the BBB to treat SAE. Dexmedetomidine activates α2A adrenoceptors on astrocytes to inhibit the extracellular release of high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) and reduce the levels of Interleukin(IL)-6 and IL-1β in brain tissue; Insulin inhibits the activity of Nuclear factor-k-gene binding (NF-κB) in astrocytes and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)s in microglia after lowering blood sugar; Citrate-covered gold nanoparticles (Cit-AuNP) or targeted inhibition of Poldip2 inhibits the nuclear translocation process of Nuclear factor-k-gene binding (NF-κB) in endothelial cells to reduce the secretion of Intercellular adhesion molecule-1(ICAM-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2); TPPU(N-[1-(1-oxopropyl)-4-piperidinyl]-N’-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-urea) inhibits Cluster of differentiation (CD)40 by inhibiting soluble epoxide hydrolase (SEH), and reduces the secretion of Tumour Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1β and IL-6; 4-aminobenzoic acid hydrazide (ABAH) or Fish oil (FO) maintain the steady state of Sphingolipid by inhibiting Myeloperoxidase (MPO); P110(an inhibitor of dynamin-related protein-1(Drp1)-Fission 1(Fis1) interaction) inhibits the Drp1-Fis1 interaction; UCF-101(an inhibitor of Omi/HtrA2) inhibits the translocation of Omi/high-temperature requirement serine protease A2 (HtrA2) from mitochondria to cytoplasm, antagonizes the Caspase-dependent apoptosis pathway and reduces poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) levels, while also protecting the tight junctions (TJs) protein; Injection of immunoglobulin G or a combination of immunoglobulin A and M inhibits complement(C)5a.