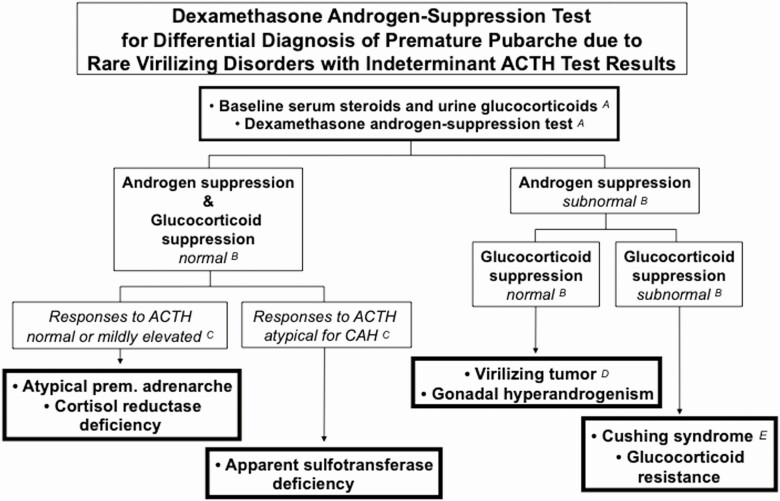
Figure 9.
Dexamethasone androgen-suppression test for rare virilizing disorders causing premature pubarche with responses to ACTH that are indeterminate (normal, elevated, or atypical for CAH) (see Fig. 8). (A) First, an early morning blood sample for testosterone, cortisol, and DHEAS and any other suspect steroid and a` 24-h urine for glucocorticoids (ie, urine free cortisol, 17alpha-hydroxycorticosteroids and/or cortisol and cortisone metabolites for quantitative steroid profiling) are obtained. Then the DAST is begun: dexamethasone, 1 mg/m2/day is given in 3 to 4 divided doses daily for 4 days, and then serum cortisol and androgens are measured on the morning of the fifth day after a final dexamethasone dose. On days 2 and 4 another 24-hr urine for glucocorticoids may be collected. If Cushing’s disease is clinically suspect, one may then begin high-dose dexamethasone (2.5 mg/m2 every 6 h) on days 2 to 4. (B) Normal androgen and glucocorticoid suppression is indicated in young children when serum testosterone falls to <10 ng/dL, DHEAS to <40 ug/dL, and cortisol to <1 µg/dL (28 nmol/L). (C) Normal androgen and glucocorticoid suppression is found in atypical premature adrenarche and in cortisol reductase deficiency or apparent CRD. Among those with responses to ACTH atypical for CAH (Fig. 8), those with apparent sulfotransferase deficiency suppress normally as well. (D) Poor androgen suppression with normal glucocorticoid suppression is characteristic of virilizing tumors and gonadal hyperandrogenism. Testosterone-secreting tumors are usually distinguishable by an abnormal pattern of testosterone precursors. Male hyperandrogenism (eg, male-limited gonadotropin-independent sexual precocity) is characterized by a male pubertal steroid pattern. (E) The elevated androgens and glucocorticoids of endogenous Cushing’s syndrome and glucocorticoid resistance are not normally suppressible by low-dose dexamethasone (ie, DAST), but those of Cushing’s disease are suppressible by high-dose dexamethasone. Assay of serum dexamethasone can be added to assess the possibility of test noncompliance if cortisol suppression is subnormal.