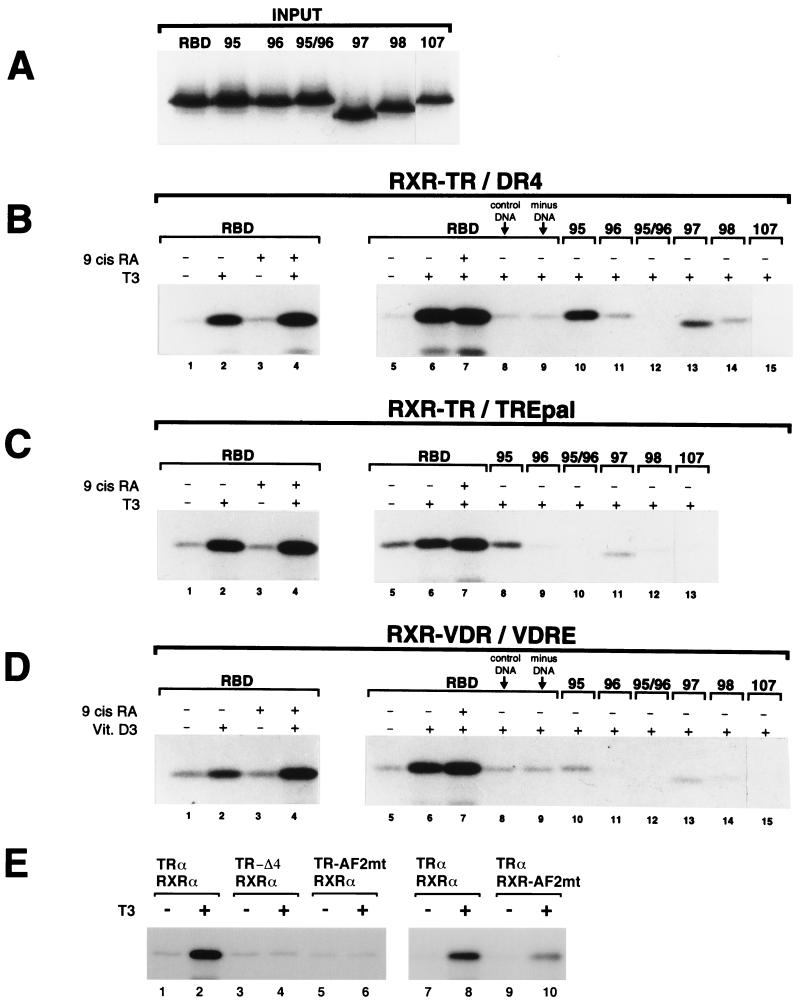
FIG. 6.
Interaction of TRAP220 RBD with DNA-bound RXR-TR and RXR-VDR heterodimers. (A) GST-RBD wild-type and GST-RBD mutant proteins (Fig. 3A) were purified and 32P-labeled (see Materials and Methods). Panel A shows 15% of the labeled input used in the experiments described below. (B and C) Both the presence and proper spacing of RBD-1 and RBD-2 are necessary for efficient binding of TRAP220 RBD to an RXR-TR heterodimer bound to a specific TRE. Unlabeled in vitro-translated hRXRα and hTRα were incubated with 32P-labeled GST-RBD wild-type or mutant proteins (panel A and indicated above the lanes) together with a biotinylated DR4 (B) or biotinylated TREpal (C) in the presence or absence of T3 or 9-cis RA as indicated. DNA-bound ternary protein complexes were precipitated by adding streptavidin-agarose beads, and the proteins were subsequently fractionated by SDS-PAGE. The reaction shown in panel B, lane 8, contained a nonspecific biotinylated DNA element (see Materials and Methods) in place of a specific TRE. The reaction shown in Fig. 6B, lane 9, did not contain any DNA. (D) Both the presence and proper spacing of RBD-1 and RBD-2 are necessary for efficient binding of TRAP220 RBD to an RXR-VDR heterodimer bound to a specific VDRE. Unlabeled in vitro-translated hRXRα and hVDR were incubated with 32P-labeled GST-RBD wild-type or mutant proteins (panel A and indicated above the lanes) together with a biotinylated VDRE (derived from the osteopontin gene promoter) in the presence or absence of 1,25-(OH)2-D3 (Vit. D3) or 9-cis RA as indicated. As above, the addition of a nonspecific DNA element or the omission of DNA altogether (lanes 8 and 9) was performed as a control. (E) The AF2 domains from both partners of a DNA-bound RXR-TR heterodimer are required for efficient binding to RBD. Unlabeled wild-type hRXRα and hTRα receptors were dimerized with TR or RXR proteins containing AF2 mutations (as indicated above the lanes) and incubated with wild-type 32P-labeled GST-RBD protein together with a biotinylated DR4 in the presence or absence of T3. Specific AF2 mutants used in this experiment include TRα-AF2mt (hTRα, E-403-K), TRα-Δ4 (C-terminal deletion of helix 12, Δ401), and hRXRα-AF2mt (F-450-A, E-453-K and E-456-K) (see Materials and Methods for details).