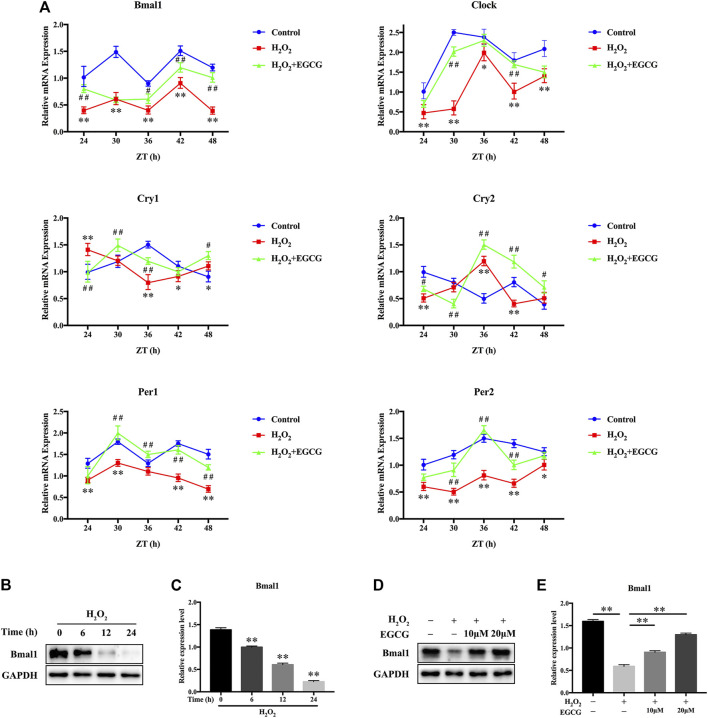
FIGURE 4.
Effects of EGCG against circadian misalignment in NPCs after exposure to H2O2. After 2 h of serum shock, NPCs were pretreated with 20 μM EGCG for 12 h after which they were treated with 300 μM H2O2 for 12 h. Then, cells were obtained for mRNA analysis between the 24 and 48 h at 6 h intervals. (A) mRNA expression levels of the circadian oscillator constituents Bmal1, Clock, Cry1, Cry2, Per1, as well as Per2 in NPCs. Transcription levels were evaluated by qPCR followed by normalization to GAPDH mRNA levels. ZT, Zeitgebers (German for “time giver”). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, indicates H2O2 vs control. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, indicates H2O2 + EGCG vs H2O2. (B) The Bmal1 expression changes after H2O2 stimulation for different times were evaluated by western blot analysis, and GAPDH was the loading control. (C) Results of densitometric analyses of the blots. (D) NPCs were pretreated with varying EGCG doses for 4 h after which they were stimulated for 24 h using H2O2. The effects of EGCG on H2O2-triggered Bmal1 expression changes were determined by western blot analysis, and GAPDH was the loading control. (E) The results of densitometric analyses of the blots. The data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.