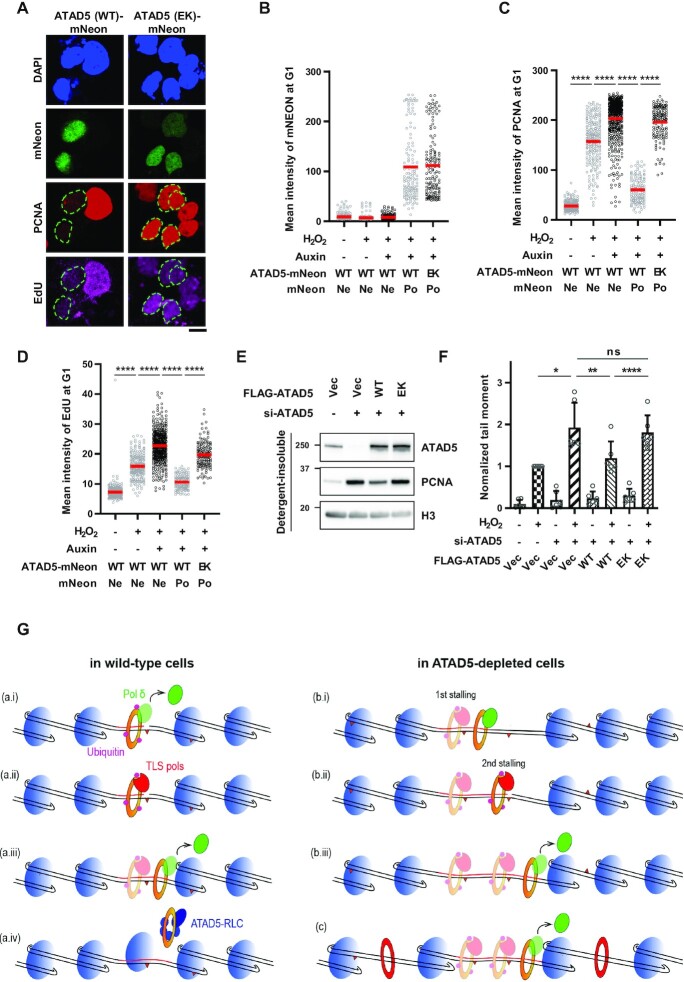
Figure 7.
PCNA-unloading-defective ATAD5 fails to restore defects in ATAD5-depleted cells. (A–D) U2OS-ATAD5AID cells were transfected with cDNA expressing mNeonGreen protein-tagged wild-type (WT) ATAD5 or PCNA-unloading-defective ATAD5 E1173K (EK) mutant for 48 h before 1 mM H2O2 treatment for 20 min with EdU incorporation. Auxin was added 12 h before H2O2 treatment. Cells were then detergent-pre-extracted and fixed for immunostaining and UDS assay. (A) Representative images of cells treated with auxin and H2O2. The dotted line represents the edge of the nucleus; scale bar: 10 μm. (B–D) mNeonGreen (B), PCNA (C) and EdU signals (D) were quantified and displayed; Ne: negative, Po: positive. (E and F) U2OS cells were transfected with a combination of WT or E1173K mutant ATAD5 (EK) cDNA and ATAD5 siRNA targeting 3′UTR for 48 h. (E) Detergent-insoluble proteins were fractionated and immunoblotted. (F) Cells were treated with 0.1 mM H2O2 for 1 h and subjected to an alkaline COMET assay. (B–D) Three independent experiments were performed and one representative result is displayed. Red bar indicates mean value. (F) Six independent experiments were normalized. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean. (B–D, F) Statistical analysis: two-tailed unpaired (B–D) and paired (F) Student's t-test (F); ****P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 and ns: not significant. (G) Graphical model for extended DNA synthesis and frequent exposure of nicks in ATAD5-depleted cells. (a) In wild-type cells treated with H2O2, (a, i) when Pol δ encounters DNA lesion on template DNA during repair DNA synthesis, it stalls and leaves from PCNA, and PCNA is monoubiquitinated. (a, ii) TLS polymerases are recruited and bypass the DNA lesion. (a, iii,iv) PCNA-Pol δ then takes over DNA synthesis until unloaded by ATAD5-RLC. After PCNA unloading, nucleosome is assembled. The remaining DNA lesions on template DNA are removed by another round of repair mechanism. (b, c) In ATAD5-depleted cells, repair DNA synthesis is extended due to the less nucleosome compaction occurred locally around clustered DNA damages (b, i) or globally (c) by PCNA remaining on DNA (red), or other yet-clear mechanism, (b, ii and c) which increases the likelihood that Pol δ will encounter DNA lesions and expose nicks. (b, iii and c) Pol δ leaves PCNA and DNA synthesis is terminated.