Scheme 1.
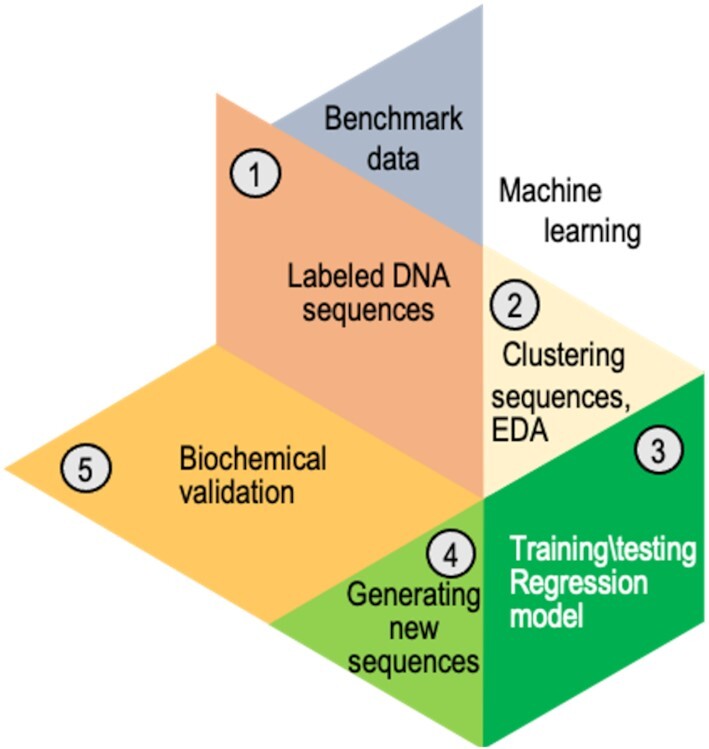
Analysis workflow after preprocessing the data from the primase–DNA binding microarray. The benchmark dataset containing DNA sequences for the training set was preprocessed (step 1). The DNA sequences were clustered into five bins using exploratory data analysis (EDA), i.e. unsupervised algorithms (step 2). A different regressor was trained for every cluster. Several regression algorithms were used; linear regression with L1 regularization provided the best results. To predict the binding scores of a new DNA sequence, the sequence was assigned to a specific bin, and its score for primase binding was predicted using that bin's regressor (step 3). Novel DNA sequences (PDRSs) with high binding score for primase were generated (step 4). It was then possible to examine the ability of those PDRSs to bind primase and induce the synthesis of RNA primers (step 5).
