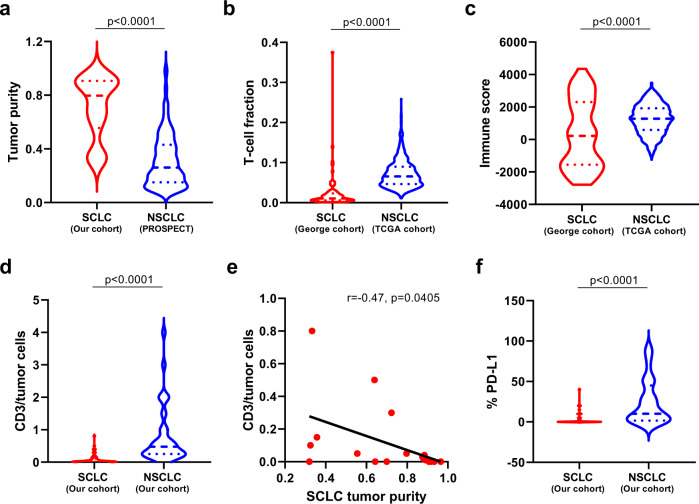
Fig. 3. Comparison of immune features in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) versus non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
a Tumor purity in SCLCs versus NSCLCs. Tumor purity was derived from whole-exome sequencing (WES) data from 19 SCLC tumors (blue) versus 242 NSCLC tumors (red) from the PROSPECT cohort. b T-cell infiltration in SCLCs compared with NSCLCs. T-cell infiltration was derived by deconvolution of RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data of 81 SCLC tumors (George cohort) versus 1027 NSCLC tumors from TCGA. c Immune score in SCLCs compared with NSCLCs. The immune score was calculated from RNA-seq data to quantify all immune cells within the tumors from 81 SCLC tumors (George cohort) versus 1027 NSCLC tumors from TCGA. d CD3 + tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) of SCLC (n = 67) versus NSCLC (n = 68) tumors by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The y axis represents CD3 + TILs: tumor-cell ratio. e Association of tumor purity with CD3 + TILs in SCLCs (n = 19). The y axis represents CD3 + TILs: tumor-cell ratio. f Expression of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) by IHC in SCLC (n = 67) versus NSCLC (n = 68) tumors. The difference of immune features between SCLC and NSCLC was evaluated using two-sided Mann–Whitney test. The correlation coefficient (r) of tumor purity with CD3 + TILs was assessed by two-tailed Spearman’s rank-correlation test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.