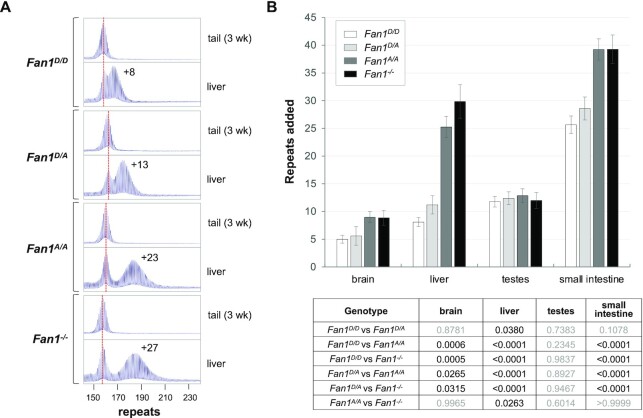
Figure 1.
A point mutation in the nuclease domain of FAN1 eliminates its protective effect against expansion in many organs. (A) Typical repeat PCR profiles from tail taken at weaning (3-week tail) and liver of 6-month old Fan1D/D, Fan1D/A, Fan1A/A and Fan1-/-mice. The dotted line represents the size of the original inherited allele as ascertained from the tail DNA taken at weaning (3-week tail). The numbers associated with some of the traces indicates the number of repeats added during the lifetime of the mouse. (B) Comparison of the number of repeats added to the original allele in different organs of 6-month old Fan1D/D, Fan1D/A, Fan1A/A and Fan1-/- mice with ∼161 repeats in the original allele. The brain data represents the average of five Fan1D/D, five Fan1D/A, five Fan1A/A and seven Fan1-/- male mice with 157–163 repeats, the data from other organs represents the average of nine Fan1D/D, five Fan1D/A, eight Fan1A/A and seven Fan1-/- male mice in the same repeat range. The error bars indicate the standard deviations of the mean. The significance of the effects were assessed using a mixed-effects model with correction for multiple testing as described in the Materials and Methods. The adjusted P values of genotype effect are listed in the table below.