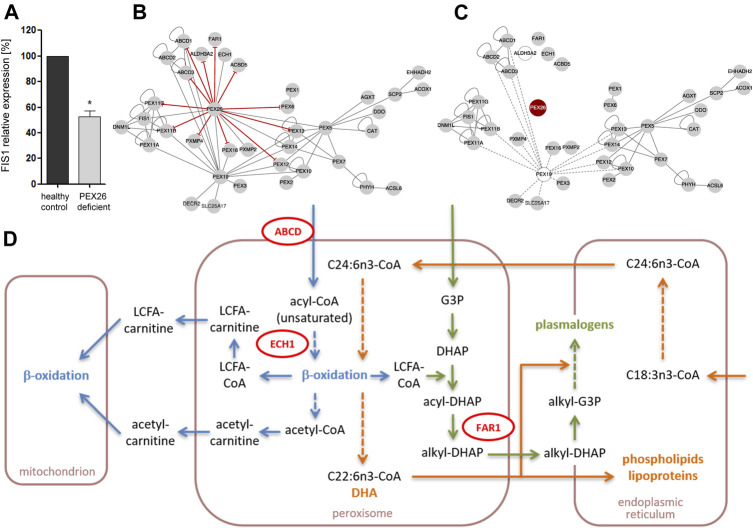
FIGURE 6.
Impact of edgetic perturbations and node removal on the PEX26 network and metabolic pathways. (A) Relative mRNA levels of FIS1 in PEX26 deficient fibroblasts (GM17398) and healthy control fibroblasts (n = 3). The expression ratios of healthy control fibroblasts were set as 100%, *p < 0.05. (B) The sites of missense variant induced edgetic perturbations on the PEX26 network are depicted by red T-arrowed edges. (C) A loss of PEX26 protein (node removal, red) disrupts the integrity of a functionally weighted PEX26 network. Proteins without contribution to intrinsic function of mature peroxisomes are depicted by clear nodes and their respective edges by dashed lines. (D) Schematic representation on key steps in β-oxidation (blue), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) metabolism (orange) and plasmalogen synthesis (green) that are shared by mitochondria, peroxisomes and the endoplasmic reticulum. Direct interaction partners of PEX26 are depicted in red (ABCD1 and ABCD3 summarized as ABCD, ECH1, FAR1). The associated pathways may be affected due to secondary dysfunction of these proteins as mediated by node removal or edgetic perturbations of PEX26. VLCFA, very long-chain fatty acids; LCFA, long-chain fatty acids; CoA, coenzyme A; G3P, glycerol-3-phosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; C18:3n3/C24:6n3, precursors of DHA (C22:6n3).