Fig. 1.
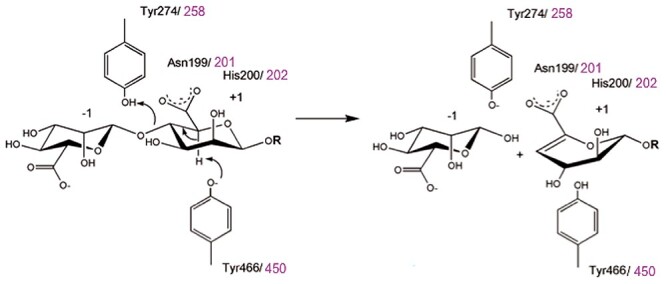
Reaction scheme for beta-elimination mechanism of alginate lyases. This catalytic mechanism is dependent on the presence of carboxylic acid groups in the substrate, which are stabilized by conserved histidine and asparagine residues in PL17 enzymes. Subsequently, a tyrosine residue abstracts a proton at C5, and finally, the formation of a double bond between C4 and C5 (beta-elimination) expels the leaving group at C4, which is protonated by a second tyrosine. Within this conserved catalytic machinery, the residue numbers are given in black for those of AlyA3, while those of Alg17c are given in magenta. This figure is available in black and white in print and in color at Glycobiology online.
