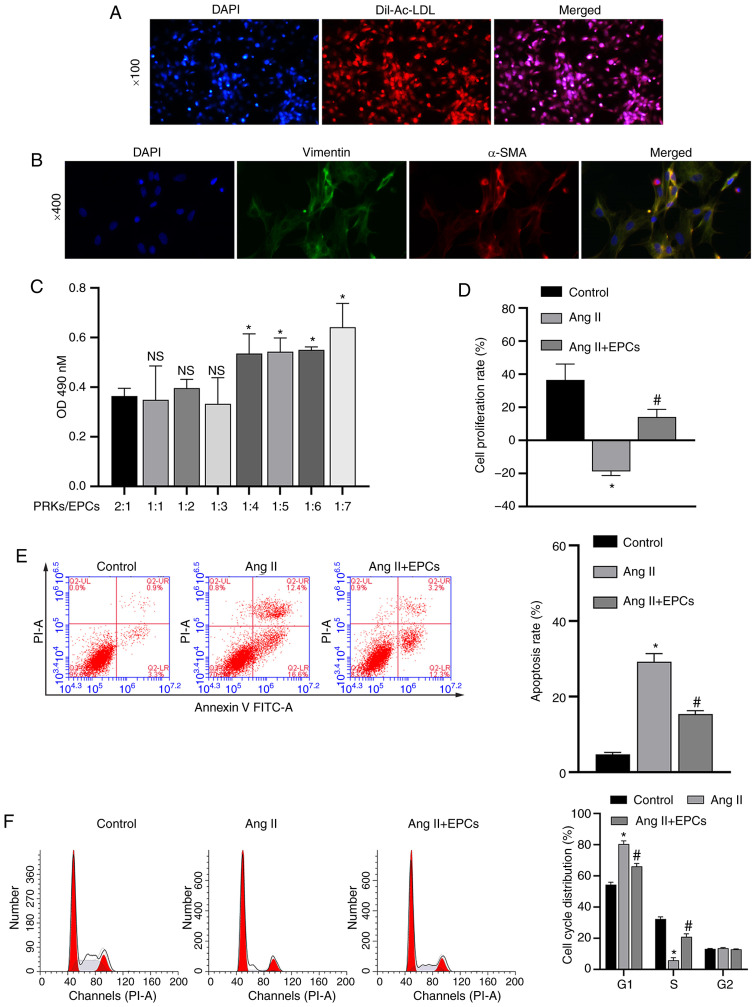
Figure 1.
Recovery of PRKs by co-culture with EPCs following injury induced by Ang II. (A) Confirmation of the isolation of EPCs via Dil-Ac-LDL staining. Magnification, ×100. (B) Confirmation of the isolation of PRKs using an immunofluorescence assay. Magnification, ×400. (C) CCK-8 analysis of the effects of different proportions of co-cultured EPCs on the proliferation of PRKs. NS P>0.05 vs. PRKs:EPCs, 2:1 group; *P<0.05 vs. PRKs:EPCs, 2:1 group. (D) CCK-8 analysis of the effects of co-cultured EPCs on the proliferation rate of Ang II-treated PRKs. FCM analysis of the effects of co-cultured EPCs on the (E) apoptosis and (F) cell cycle of Ang II-treated PRKs. *P<0.05 vs. Control; #P<0.05 vs. Ang II. Ang II, angiotensin II; EPCs, endothelial progenitor cells; PRKs, primary rat kidney cells; FCM, flow cytometry; CCK-8, Cell Counting Kit-8; Dil-Ac-LDL, Dil complex acetylated low-density lipoprotein; OD, optical density; α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; NS, not significant.