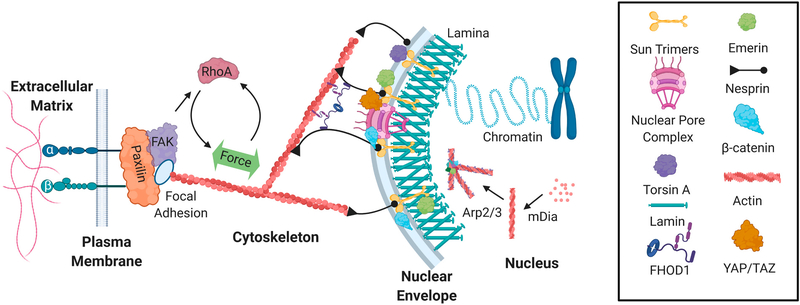
Fig. 2.
The nucleoskeleton structurally and functionally couples the genome to extracellular dynamics. Extracellular forces activate integrin and focal adhesion signaling to increase F-actin contractility, which leads to increased polymerization of the actin cytoskeleton. LINC complexes composed of Sun trimers and Giant Nesprin mechanically couple the actin cytoskeleton and regulate the access of important mechanical transducers such as βcatenin and YAP/TAZ. Mechanical coupling of actin and LINC involves a cytoplasmic formin FHOD1 that attaches nesprin and actin at multiple points for a more robust association. Torsin A may also facilitate the LINC assembly at the nuclear envelope. Emerin associates with both sides of the nuclear envelope to regulate extra and intranuclear actin dynamics. Inside the nucleus, G-actin is assembled into linear and branched networks to regulate chromatin dynamics and gene access.