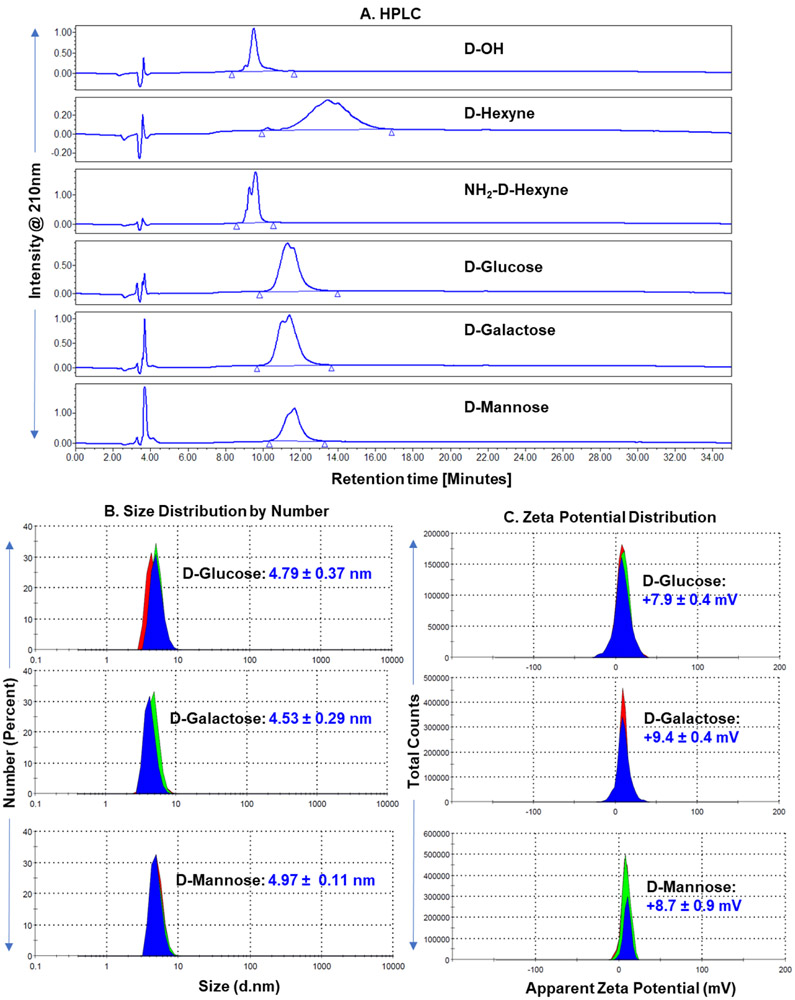
Figure 3. Physio-chemical characterization of dendrimer conjugates.
A. HPLC comparison of parent hydroxyl dendrimer (D-OH, RT: 9.5 min), alkyne-terminating dendrimer (D-Hexyne, RT: 13.4 min), trifunctional dendrimer (NH2-D-Hexyne, RT: 9.6 min), and sugar modified dendrimers (D-Glucose, RT: 11.3 min; D- Galactose, RT: 11.4 min; and D- Mannose, RT: 11.7 min). All the intermediates and sugar conjugates have >99% purity. B. Hydrodynamic diameter measurements of D-Sugars via dynamic light scattering. The dendrimer conjugates show a slight increase in size from D-OH (~4 nm). C. Representation of zeta potential distribution measurements of D-Sugars showing nearly neutral zeta potential.