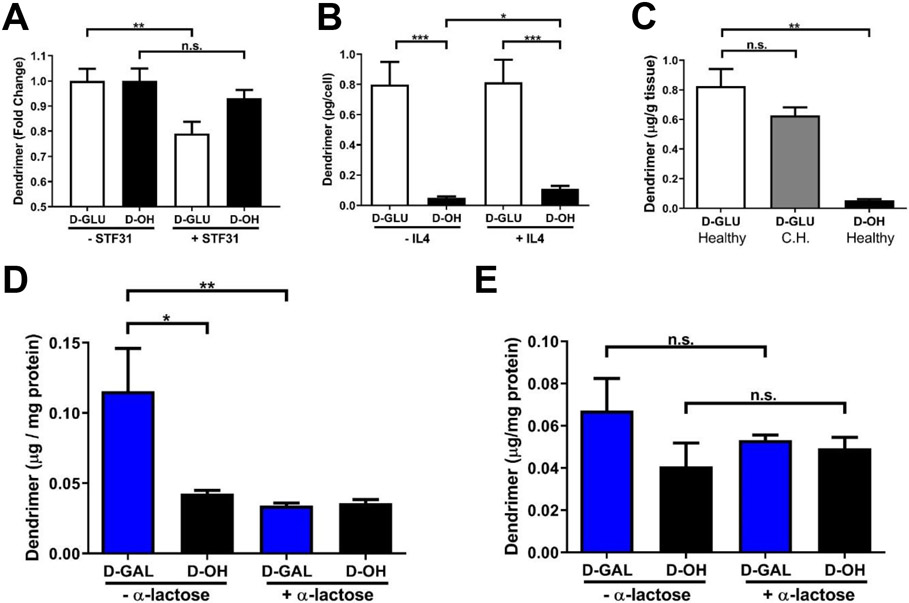
Figure 7. Dendrimer-glucose and -galactose conjugates alter cellular interactions.
A) Blocking GLUT-1 receptors on BV2 murine microglia by STF-31 reduces dendrimer-glucose (D-GLU) cellular internalization but does not impact uptake of unmodified dendrimers (D-OH), validating the GLUT-1 uptake mechanism of D-GLU. ** p < 0.01D, n.s. p > 0.1. B) Dendrimer internalization in IL4 and resting microglia is significantly greater with D-GLU than D-OH, indicating improved cellular internalization. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001. C) D-GLU exhibits similar brain uptake in healthy brain tissue and in the contralateral hemisphere of tumor-bearing brains and significantly greater than D-OH, indicating increased blood brain barrier penetration. ** p < 0.01, n.s. p > 0.1. D) Dendrimer-galactose conjugates (D-GAL) exhibits significantly greater membrane association in GL261 murine glioma cells than D-OH. Blocking of galectins with α-lactose knocks membrane levels of D-GAL down to similar levels as D-OH, validating D-GAL interactions with galectin surface receptors. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. E) Cellular uptake of dendrimers of D-GAL is not altered with α-lactose treatment, indicating that D-GAL interactions with galectin receptors does not impact cellular internalization. n.s. p > 0.1.