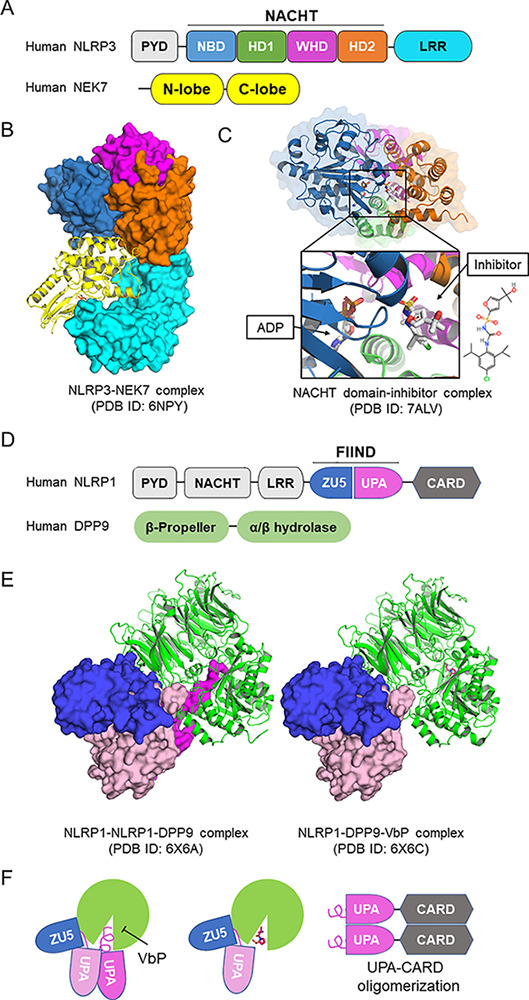
Structures of NLRP1 and NLRP3. (A) Domain architecture of NLRP3. NLRP3 is composed of an N-terminal pyrin domain (PYD); a central NACHT domain that is subdivided into NBD, helical domain 1 (HD1), winged helix domain (WHD), and helical domain 2 (HD2); and a C-terminal LRR domain. (B) Structure of monomeric NLRP3 in complex with NEK7 solved by cryo-EM (Protein Data Bank [PDB] ID: 6NPY). The structure is colored coded as in A by domains. (C) Crystal structure of NACHT domain of NLRP3 in complex with ADP and a small molecular inhibitor (PDB ID: 7ALV). The inhibitor locates at the multiple domain interface and locks protein in the inactive conformation. (D) Domain architecture of NLRP1 and DPP9. The autocatalytic FIIND is composed of ZU5 and UPA subdomains. (E) Cryo-EM structures of the ternary complex of NLRP1-NLRP1-DPP9 and the inhibition by VbP. In the ternary complex (left, PDB ID: 6X6A), two NLRP1 molecules bind to one DPP9 (green). The first NLRP1 has intact FIIND in which the ZU5 subdomain (blue) associates with the UPA subdomain (pink). The second NLRP1 has the UPA subdomain dissociated, and the N-terminal peptide of the UPA subdomain inserts into the DPP9 catalytic pocket (magenta). Vbp binding displaces the inserted N-terminal UPA peptide and reduces second UPA occupancy (PDB ID: 6X6C). (F) UPA-CARD released from DPP9 initiates inflammasome assembly.
