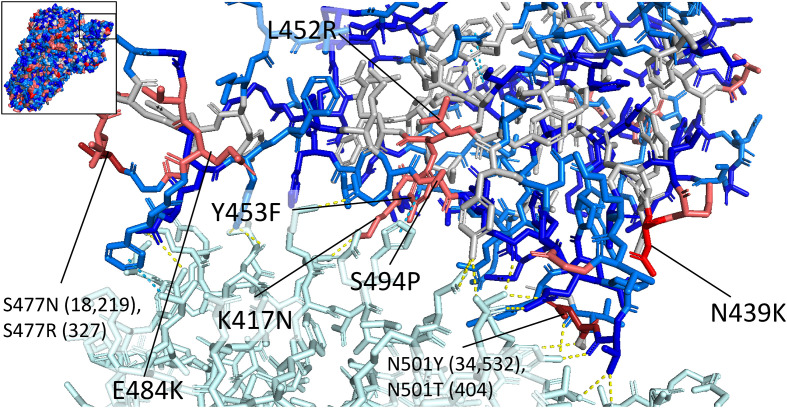
Fig. 4.
Structure of the interface between the spike receptor binding domain (RBD) and the human ACE2 receptor (top left shows the location of the RBD on the spike protein). The ACE2 receptor is shown in light cyan, and the spike residues are colored according to the frequency of variation: red is used for residues with variants in more than 1000 sequences, pink is used for variant frequencies of 100–1000, light blue for frequencies of 10–100, blue for frequencies of 2–10, and grey for residues with no observed variants. Residues mutated in more than 100 sequences are labeled with the one-letter codes of the reference residue and the most commonly observed mutation. If multiple mutations are observed in the same residue in more than 100 sequences, each mutation is listed with the number of sequences with the mutation in parentheses. Direct contacts are shown with dotted lines: hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are shown in yellow, and pi-pi stacking interactions are shown in cyan. The residue Y453 forms pi-pi stacking interactions with the ACE2 residue H34. The mutation Y453F would result in the loss of a hydroxyl group, which may reduce steric clashing with the histidine residue. N439 does not directly contact the receptor binding domain, though it is believed that the variant lysine residue, which is positively charged, could form a salt bridge with the negatively charged ACE2 residue E329, increasing binding affinity of the RBD to ACE2 (Wu et al., 2021). The substitution L452R is observed in the Epsilon variant of concern. The mutation of a hydrophobic leucine side chain to a positively charged arginine side chain will affect electrostatic properties at the site of the mutation, which may affect antibody binding. The substitution E484K involves the replacement of a negatively charged glutamic acid residue with a positively charged lysine residue, which results in decreased efficacy of antibodies produced against wild-type E484 variants (Liu et al., 2021a; Garcia-Beltran et al., 2021). PDB structures used: PDB ID: 6M17 (RBD-ACE2 interface), PDB ID: 6VSB (whole spike protein on upper left). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)