Figure 5.
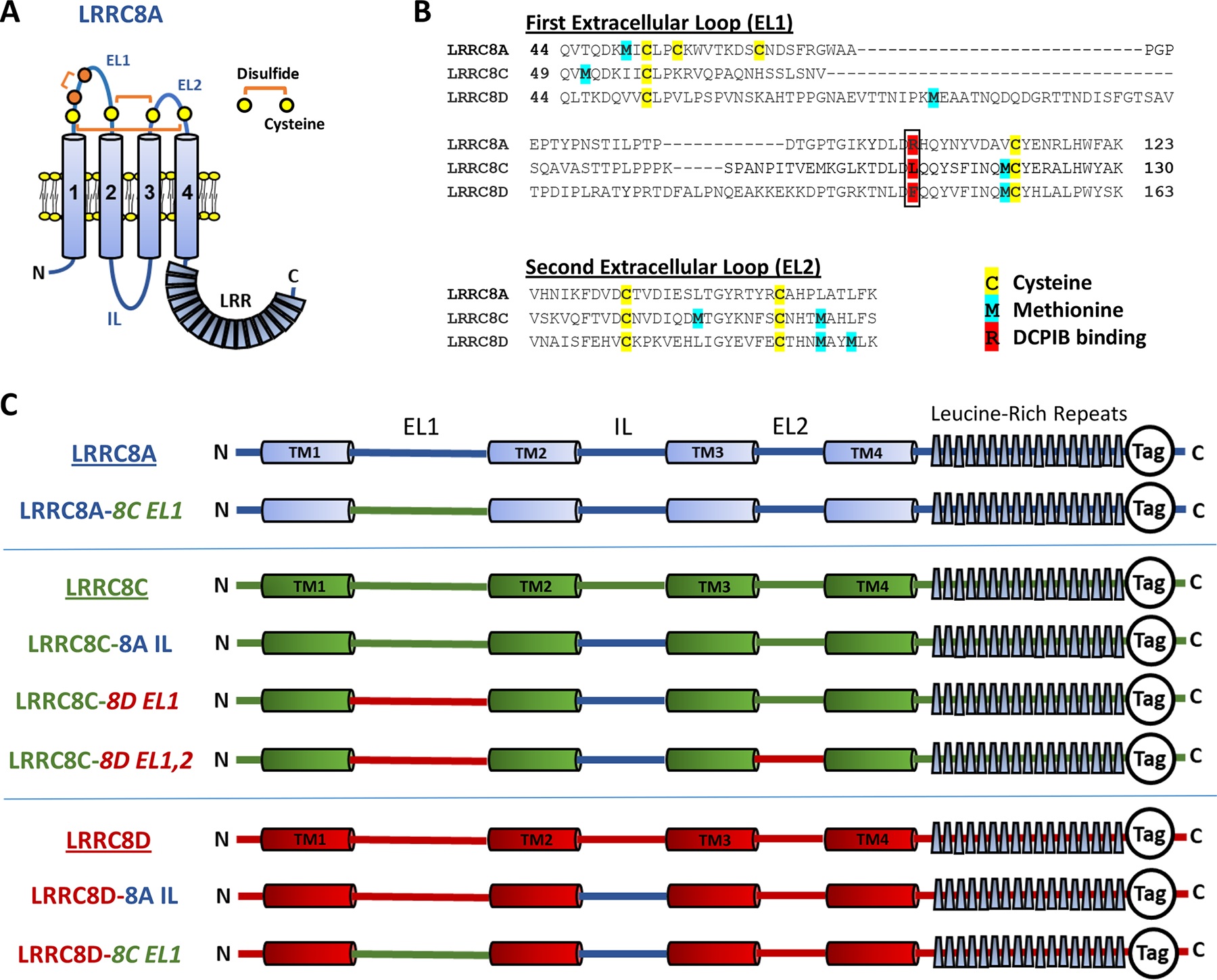
A, Schematized topography of an LRRC8A monomer. The first extracellular loop (EL1) contains two conserved (C1, C4; yellow) and two non-conserved cysteines (C2, C3; orange). C1 and C4 form disulfide bonds with conserved cysteines in EL2, as shown. C2 and C3 form a third disulfide within EL1. The intracellular loop (IL, blue) sequence (P147-R262) of LRRC8A was substituted for the homologous regions of LRRC8C and 8D for the experiments shown in Figs. 8, 10, and 11. B, The EL1 and EL2 amino acid sequences for LRRC8A, C, and D, with potential redox-responsive cysteines (yellow) and methionines (blue) highlighted. R108 (red, boxed) of LRRC8A is implicated in DCPIB binding and block of LRRC8A homohexameric channels (Kern et al., 2019). LRRC8C and 8D have lysine and phenylalanine, respectively, in the analogous position. C, Structure and nomenclature of the C-terminal tagged LRRC8 “wild-type” and chimeric constructs utilized in this study. LRRC8A sequence in shown in blue, LRRC8C in green, and LRRC8D in red. All chimeras included the 8A IL substitution. EL1 and EL2 substitutions are indicated in italics. Tag refers to either monomeric GFP or mCherry fluorescent proteins.
