Figure 2. EM and crystal structures of EBV and CMV entry complexes.
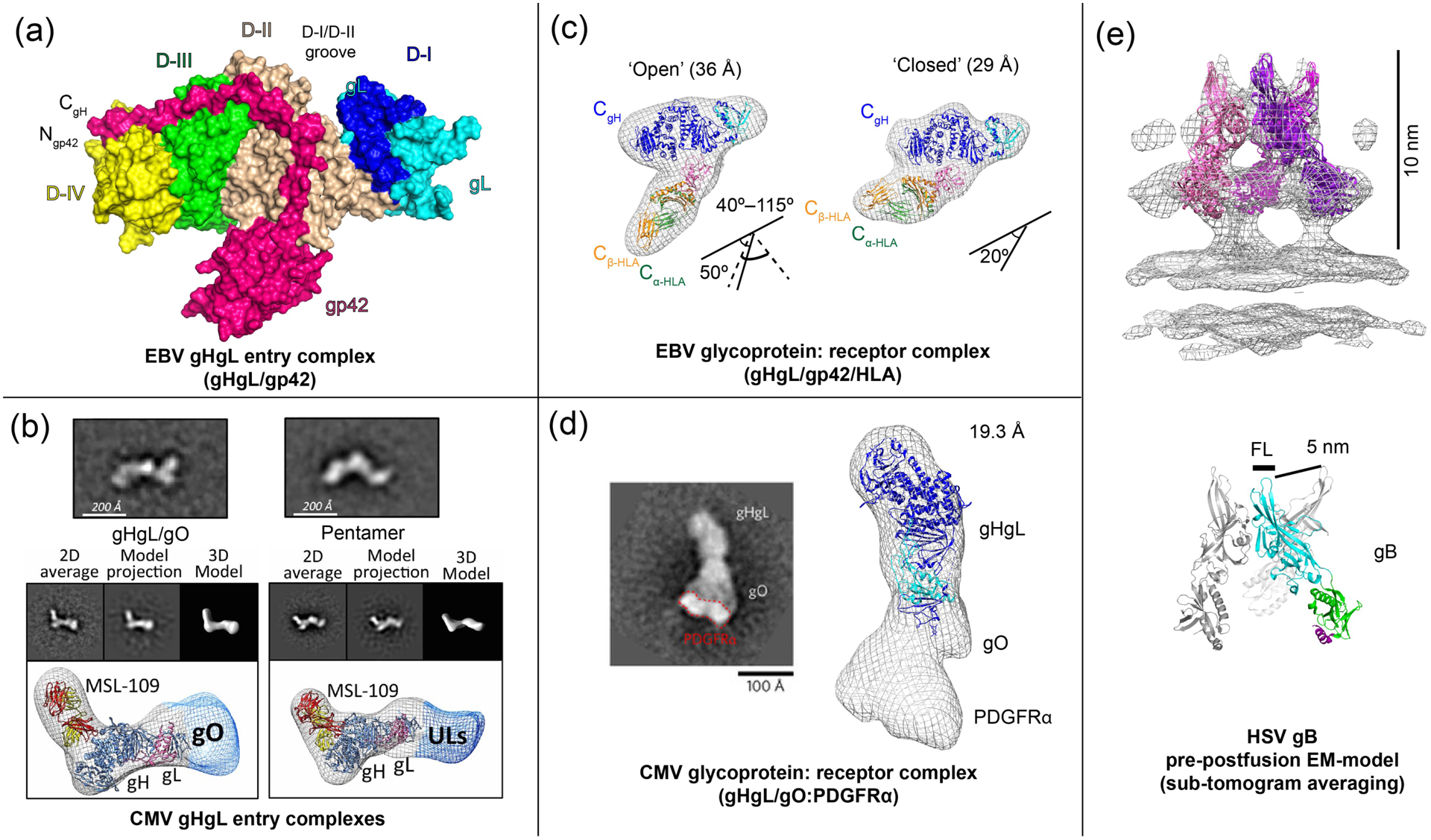
(a) The crystal structure of the EBV gHgL/gp42 complex (PDB ID: 5T1D) [22], showing interactions of the extended gp42 N-terminal domain and location of the HLA-binding gp42 C-terminal domain. (b) CMV gHgL forms gHgL/gO trimers and gHgL/UL128/UL130/UL131 Pentamers through its N-terminal domain, as visualized by negative stain EM [17]. (c) EM structure of EBV gHgL/gp42 in complex with HLA receptor [22,41]. (d) The EM structure of the CMV gHgL/gO trimer in complex with PDGFRα receptor model (EMD-3391) [23]. (e) A ‘pre-postfusion’ HSV-1 gB model derived from sub-tomogram averaging of intact gB on vesicles (EMD-3362) [42]. Figures adapted from original publications and public databanks as cited. Other structures were rendered in Chimera (UCSF) and MacPymol (Schrödinger LLC).
