Fig. 1.
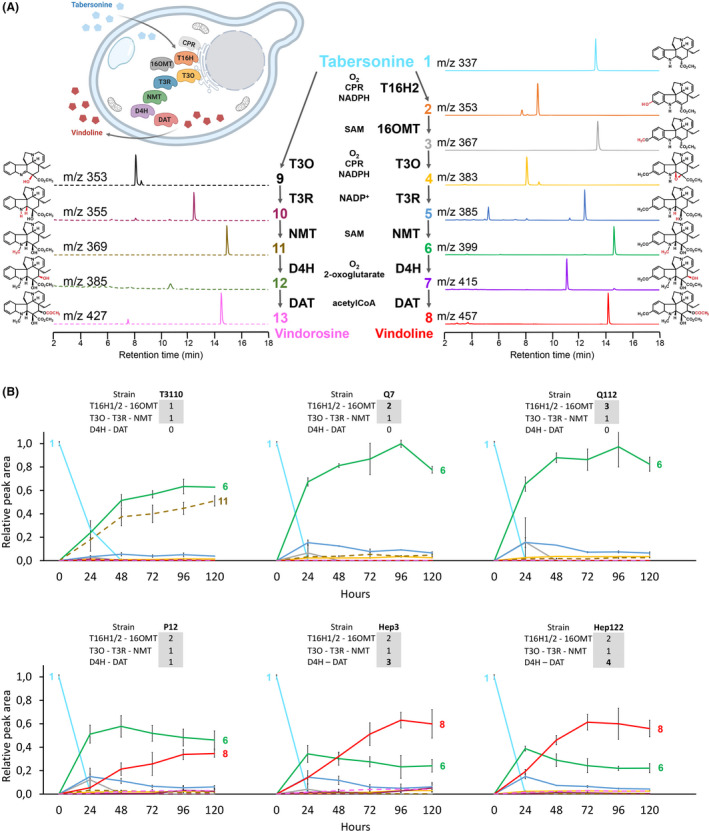
Tailoring yeast cell factories for vindoline bioproduction.
A. Vindoline biosynthetic pathway and parallel branch vindorosine pathway. Each colour and number correspond to enzyme product, represented by molecular structure, chromatogram, m/z and retention time: 1 tabersonine, 2 16‐hydroxytabersonine, 3 16‐methoxytabersonine, 4 16‐methoxytabersonine epoxide, 5 16‐methoxy‐2,3‐dihydro‐3‐hydroxytabersonine, 6 desacetoxyvindoline, 7 deacetylvindoline, 8 vindoline and the by‐products 9 tabersonine imine alcohol, 10 2,3‐dihydro‐3‐hydroxytabersonine, 11 desacetoxyvindorosine, 12 deacetylvindorosine and 13 vindorosine. MS/MS fragmentation patterns of compounds are presented in Table S1. Cofactors are indicated for each enzyme.
B. Time‐course monitoring of extracellular metabolite content in generated S. cerevisiae strains. The feedings were performed with 125 µM of tabersonine in the initial 200 µl of YPD/strain/time point. The names and the number of gene copies integrated into each strain are written on the top of each graphic. The curves represent the means of peak areas relative to tabersonine. Error bars: standard deviation (n = 3 biological replicates). By‐products are shown in dashed lines.
