Fig. 1.
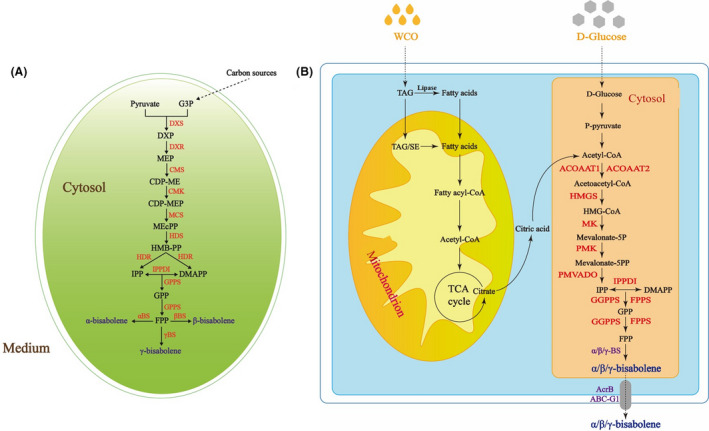
Biosynthesis pathway for bisabolene production in the yeast Y. lipolytica and biosynthesis pathway for bisabolene production in the plants.
A. Biosynthesis pathway for bisabolene production in plants. Plants produce FPP via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway from pyruvate and glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate. The endogenous MEP pathway enzymes are shown in red. DXS: DXP synthase, DXR: DXP‐reductoisomerase, CMS: MEP cytidylyltransferase, CMK: CDP‐ME kinase, MCS: MECDP synthase, HDS: (E)‐4‐hydroxy‐3‐methylbut‐2‐enyl‐diphosphate synthase, HDR: HMBPP reductase, IPPDI: isopentenyl‐diphosphate delta‐isomerase, GPPS: geranyl diphosphate synthase, αBS: α‐bisabolene synthase, βBS: β‐bisabolene synthase, γBS: γ‐bisabolene synthase.
B. Biosynthesis pathway for bisabolene production in the yeast Y. lipolytica. Yeast rely on the MVA pathway to produce FPP from acetyl‐CoA. Since the bisabolene synthase (BS) is not present in Y. lipolytica, to construct a complete bisabolene pathway in Y. lipolytica, three heterologous genes encoding α‐bisabolene synthase (αBS, from A. grandis), β‐bisabolene synthase gene (βBS, from Z. officinale) and the γ‐bisabolene synthase gene (γBS, from H. annuus) were introduced. The endogenous MVA pathway enzymes and the heterologous enzymes that were overexpressed in the engineered Y. lipolytica strains are shown in red and purple respectively. αBS: α‐bisabolene synthase, βBS: β‐bisabolene synthase, γBS: γ‐bisabolene synthase ACOAAT1: acetyl‐CoA C‐acetyltransferase 1, ACOAAT2: acetyl‐CoA C‐acetyltransferase 2, HMGS: hydroxymethylglutaryl‐CoA synthase, HMGR: hydroxymethylglutaryl‐CoA reductase, MK: mevalonate kinase, PMK: phosphomevalonate kinase, PMVADO: diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase, IPPDI: isopentenyl‐diphosphate delta‐isomerase, GGPPS: geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase, type III, FPPS: farnesyl diphosphate synthase.
