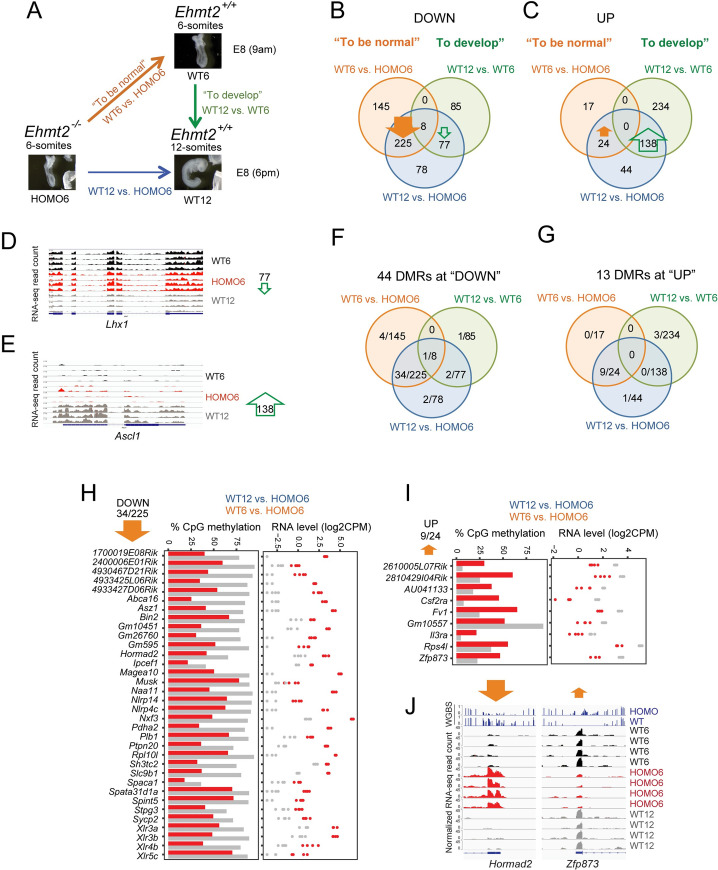
Fig 2. A three-way comparison reveals the direct effects of zygotic Ehmt2 mutation and identifies false positives of the conventional method that compares siblings.
(A) Three-way comparison. The conventional comparison (blue arrow) is normally made between uterus-mate mutant and wild type embryos. Because the mutant is developmentally delayed, the differences between these uterus-mates can be divided into two components: 1) “what it takes to be normal” (orange arrow), and 2) “what it takes to develop” from stage one to stage two (green arrow). We illustrate this idea by comparing 6-somite Ehmt2−/− (HOMO6) and 6-and 12-somite Ehmt2+/+ (WT6 and WT12) embryos. (B-C) Results of the RNA-seq experiment are displayed after a 3-way comparison. Venn diagrams depict the number of DEGs along the blue, orange, and green arrows inside the circles of the matching color. (B) Genes are downregulated in the condition where the arrow points. EHMT2 is required to suppress 225 genes in WT6 and WT12 embryos (thick arrow). (C) Genes are upregulated in the condition where the arrow points. 138 DEGs require EHMT2 according to the WT12-HOMO6 comparison. Because these are also required to reach the 12-somite stage from 6-somite stage in the WT embryos (WT12-WT6 comparison), these DEGs are false positives in the conventional comparison. (D-E) IGV browser views are shown of normalized RNA-seq reads at false positive DEGs with reduced (Lhx1) or increased (Ascl1) expression from WT6 to WT12. (F-J) DNA methylation changes occur at a specific subset of DEGs. WGBS analysis in 9.5 dpc WT versus HOMO embryos identified 57 DMRs at the TSS of DEGs. Venn diagrams (F and G) depict the subset of DEGs, which are differentially methylated. (H-I) CpG methylation level (left) and RNA expression level (right) are plotted at DEGs with TSS DMR from the most populated sections of the Venn diagrams displayed in F and G. Some require EHMT2 for DNA methylation at the TSS and for gene silencing (H), others require it for the TSS hypomethylation, and expression (I). Grey, WT; red, HOMO. (J) IGV browser views are shown of DNA methylation and RNA expression levels at DEGs with reduced (Hormad2) or increased (Zfp873) DNA methylation in the mutant.