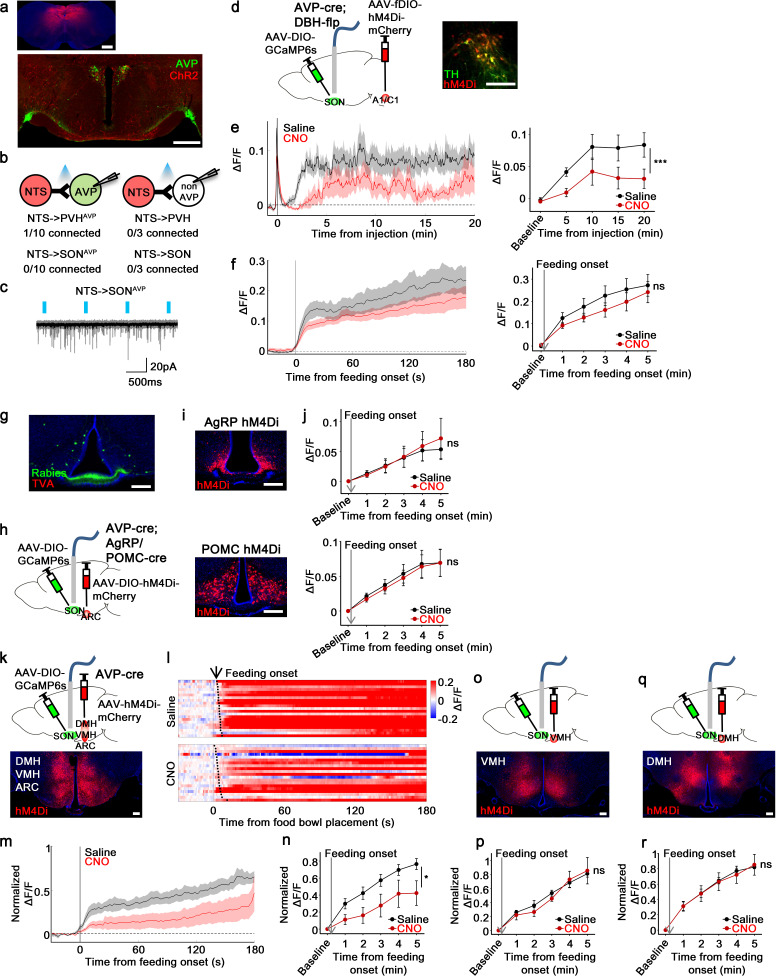
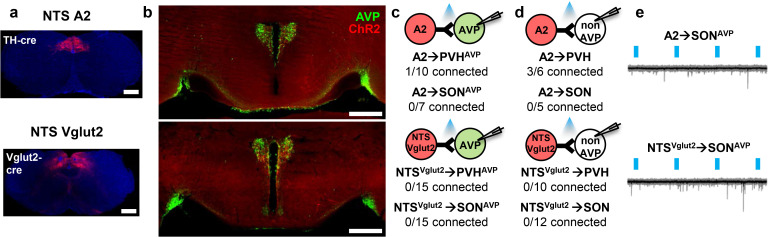
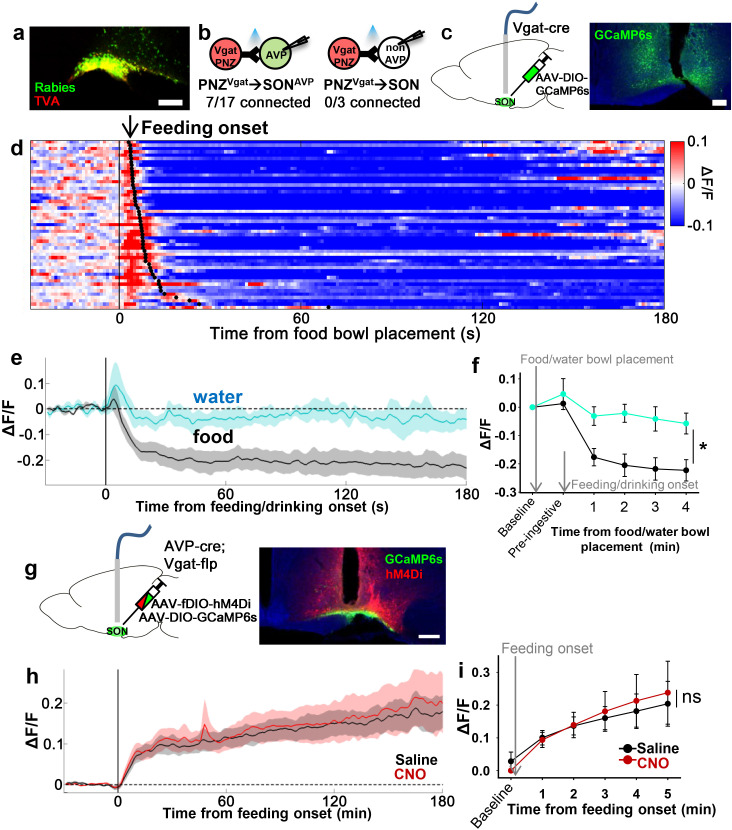
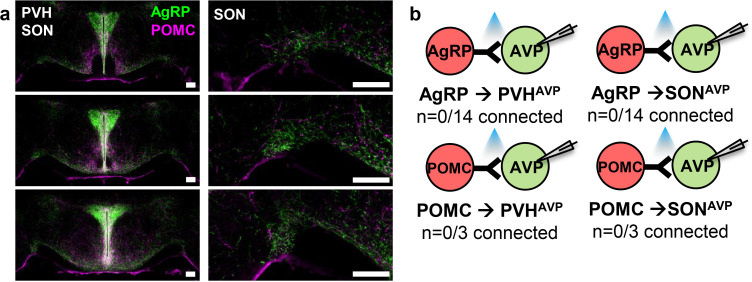
Figure 7. non-AgRP/POMC neurons in the ARC mediate food-related presystemic regulation of SONAVP neurons.
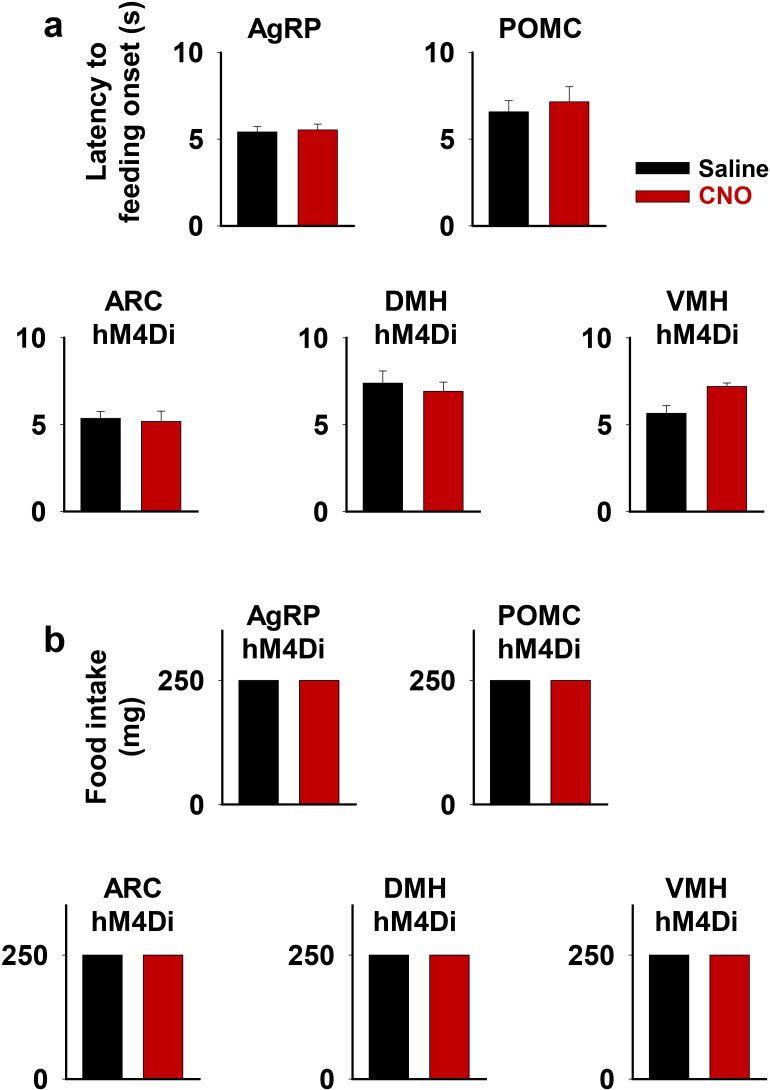
(a) Representative images showing expression of ChR2-mCherry in the NTS (top), and their efferent projections in the PVH and SON (bottom). (b) Number of PVHAVP and SONAVP neurons (left), and non-GFP PVH and SON neurons (right) receiving direct synaptic inputs from the NTS. (c) Representative traces showing light-evoked responses. Black trace is an average of all traces (gray) in consecutive trials. (d) Schematic of SONAVP photometry experiment with hM4Di-mediated inhibition of A1/C1 neurons. (e) Average SONAVP population activity to hypotension induced by vasodilating drug HDZ in saline and CNO trials (left). Data binned every 5 min (right). ***p<0.001; RM two-way ANOVA, p<0.001, n=9 mice. (f) Average SONAVP population activity in response to feeding onset in saline and CNO trials (left). Data binned across feeding periods (right). ns, p>0.05; RM two-way ANOVA, p>0.05, n=16 mice. (g) Representative image showing rabies-labeled neurons in the ARC that are monosynaptically connected to magnocellular SONAVP neurons. (h) Schematic of SONAVP photometry experiment with hM4Di-mediated inhibition of AgRP or POMC neurons. (i) Representative images showing hM4Di expression in AgRP (top) and POMC neurons (bottom). (j) Average SONAVP population activity binned across feeding periods in saline and CNO trials of AVP-IRES-Cre;Agrp-IRES-Cre (top) and AVP-IRES-Cre;Pomc-IRES-Cre (bottom) mice. ns, p>0.05; RM two-way ANOVA, p>0.05 (AgRP), p>0.05 (POMC), n=4 (AgRP), 8 (POMC). (k, o, q) Schematic of SONAVP photometry experiment with hM4Di-mediated non-specific inhibition of the ARC+VMH+DMH (k), VMH only (o), and DMH only (q). (l) Single-trial timecourses of SONAVP population activity in response to food bowl placement in saline and CNO trials of ARC+VMH+DMH group. Trials are sorted according to latency from food bowl placement to feeding onset (black ticks). n=5 mice. (m) Average SONAVP population activity in response to feeding onset in saline and CNO trials of ARC+VMH+DMH group. n=9 mice. (n, p, r) Average SONAVP population activity binned across feeding periods in saline and CNO trials of ARC+VMH+DMH (n), VMH only (p), and DMH only (r) groups. ns, p>0.05; *p<0.05; RM two-way ANOVA, p=0.033 (ARC+VMH+DMH), p>0.05 (VMH only), p>0.05 (DMH only), n=5 (ARC+VMH+DMH), 4 (VMH only), 7 (DMH only) mice. Scale bars, 500 µm (a, d), 200 µm (g, i, k, o, q). Values are means ± SEMs across mice. See also Figure 7—figure supplements 1–4. AVP, vasopressin; DMH, dorsomedial nuclei; SON, supraoptic nuclei; VMH, ventromedial.