Fig. 1.
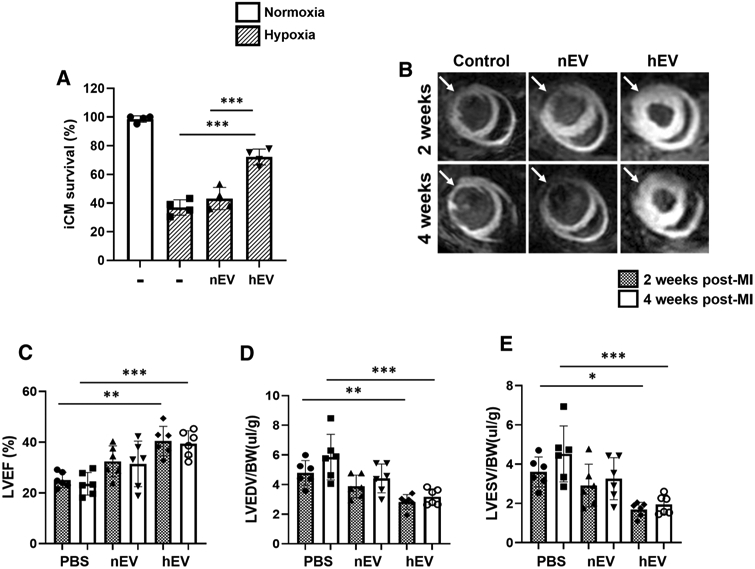
Hypoxic iCM-derived EVs enhance iCM survival and murine myocardial viability. a Survival rate of iCMs was measured by MTT analysis after hypoxic insult. EVs were isolated from the in vitro supernatant of iCMs exposed to hypoxic conditions (< 1% O2; hEVs), and normoxic condition (20% O2; nEVs). The iCMs were exposed to 50 μg of the corresponding EVs during hypoxic insult (< 1% O2, 5% CO2, 94% N2) for 18 h. The experimental groups consisted of four conditions: normoxia control, hypoxia control, hypoxia with nEV treatment, and hypoxia with hEV treatment. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons and mean data ± SD (n = 4). b Manganese-enhanced MRI of SCID mice myocardium was performed at weeks 2–4 post-MI. The treatment groups consisted of (1) normal saline control, (2) nEVs, and (3) hEVs (white arrows point to the infarcted area). c-e Left-ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), left-ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), and left-ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV) measurements of saline control (n = 6), nEVs (n = 6), and hEVs (n = 6) treatment groups. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons and mean data ± SD. Statistically non-significant comparisons are not shown. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001
