Figure 2.
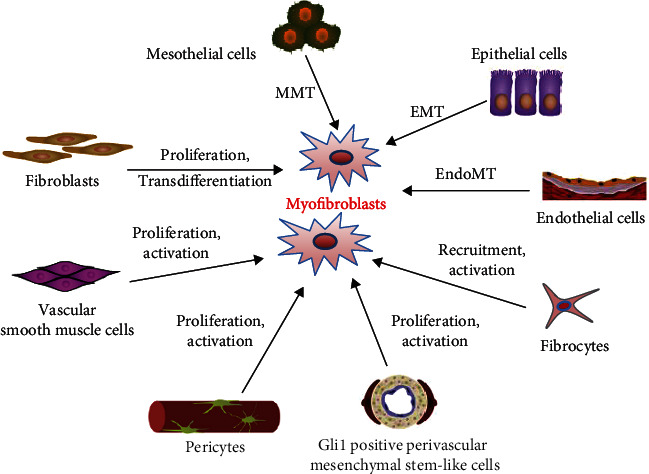
Potential sources and formation mechanisms of myofibroblasts. Activated myofibroblasts are central drivers for fibrosis and can secrete excess extracelluar matrix proteins. The cellular subsets may be originated from resident fibroblasts, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, circulating fibrocytes, mesothelial cells, vascular smooth muscle cells, pericytes, Gli1 positive perivascular mesenchymal stem-like cells, and others. Diverse mechanisms comprising cellular proliferation, activation, transdifferentiation, recruitment, mesothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (MMT), epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) can lead to myofibroblast formation [adapted from refs. [11, 15]].
