Figure 5.
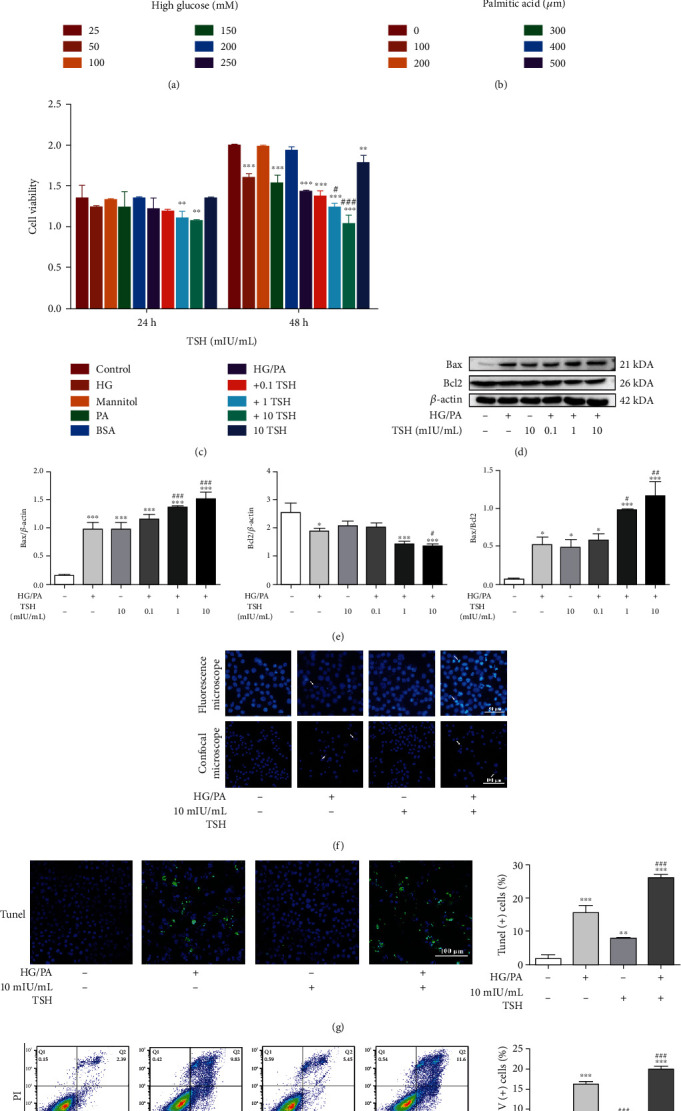
Neurodamage effect of TSH on HG/PA-induced glucolipotoxicity in RSC96 cells. (a) High glucose-induced cytotoxicity (n = 3). (b) Cell viability under varied concentrations of palmitic acid (n = 3). (c) Cell viability under HG/PA with or without different TSH concentrations. HG: 50 mM high glucose; mannitol: 50 mM mannitol; PA: 300 μM palmitic acid (n = 3). (d–e) Bax and Bcl2 protein expression under HG and PA or TSH treatments (n = 3). TSH enhanced Bax expression and inhibited Bcl2 expression in a dose-dependent manner. Hoechst staining was performed to determine nuclear morphology. Representative micrographs corresponding to three independent experiments based on fluorescence microscopy or confocal microscopy. (f) Nuclear condensation (white arrows, n = 3). Apoptosis detected via (g) TUNEL staining and (h) Annexin V-FITC/PI assay (n = 3). All data are presented as mean ± SD (∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001, compared with untreated cells; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001, compared with HG/PA-treated cells).
