FIGURE 10.
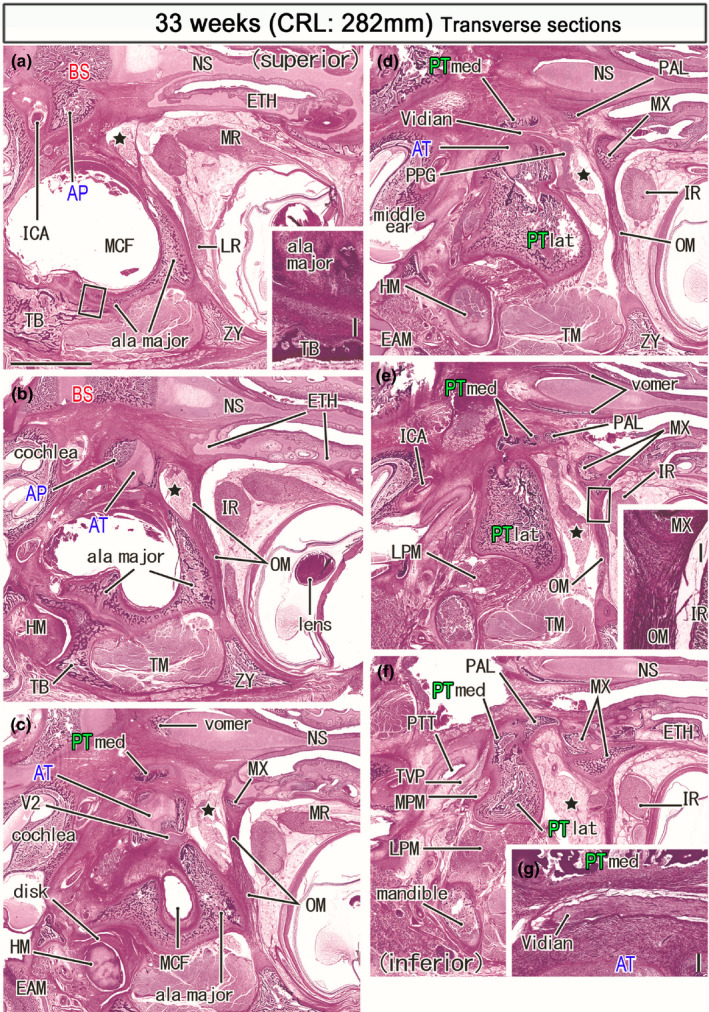
Horizontal sections of a specimen at 33 weeks (282 mm CRL). Panel (a) displays the uppermost section, while panel (f) the lowermost. Intervals between panels are 0.8 mm (a, b), 0.7 mm (b, c), 0.6 mm (c, d), 0.5 mm (d, e) and 0.7 mm (e, f). The bony alar process (AP) connects to the basisphenoid (a) medially and the ala temporalis laterally (AT; panel b). A bulky membranous bone of the greater wing (ala major) faces the zygomatic bone (ZY; panel a), the squamous portion of the temporal bone (TB; panels a and b), and a disk of the temporomandibular joint (panels c). The PT‐med carries the top in panel (c), faces the Vidian nerve in panel (d), divides into four pierces in panel (e) and, attaches to the PT‐lat in panel (f). The orbital muscle (OM) extends from the greater wing to the ethmoid (ETH; panel b) and the maxilla (MX; panels c). The smooth muscle also extends between the maxilla and zygomatic bone (panels d and e). The pterygopalatine fossa (star) is large and separated from the orbit by the orbital muscle (OM). Panel (g) shows a higher magnification view of the Vidian nerve in panel (d). Insert in panels (a) and (e) corresponds to a square in the panel, respectively. Panels (a–f) are prepared at the same magnification (scale bar: 5 mm in panel (a); 0.2 mm in two inserts and panel (g). Other abbreviations, see the common abbreviation
