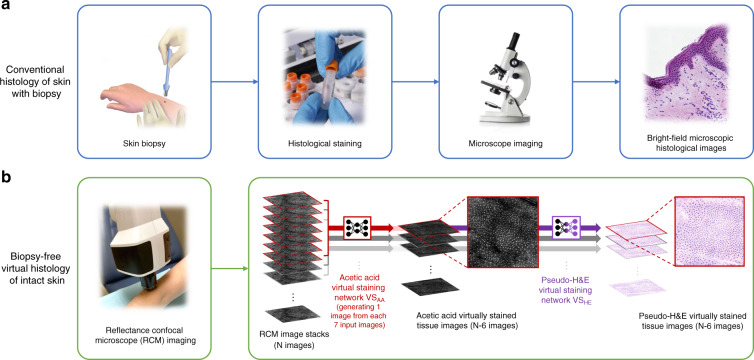
Fig. 1. The schematic diagram demonstrating the conventional (top) and biopsy-free virtual (bottom) histological staining procedures for skin pathology.
(a) Standard tissue biopsy, followed by tissue fixation, processing, and staining results in microscopy slides for pathological interpretation. (b) By employing the trained deep neural network that takes a stack of RCM images of unstained intact skin as input and instantly generates corresponding virtually stained tissue images, the reported deep learning-based virtual histology of skin may provide a unique avenue to biopsy-free, label-free clinical dermatological diagnosis. Each time, a stack of seven axially adjacent RCM images is fed into a trained deep neural network VSAA and transformed into an acetic acid virtually stained tissue image that is corresponding to the central image of the input stack, so that a stack of N images can be used to generate N-6 virtually stained 3D output images that are axially adjacent. Following this acetic acid virtual staining, a pseudo-H&E virtual staining step is further performed by a trained deep neural network (VSHE).