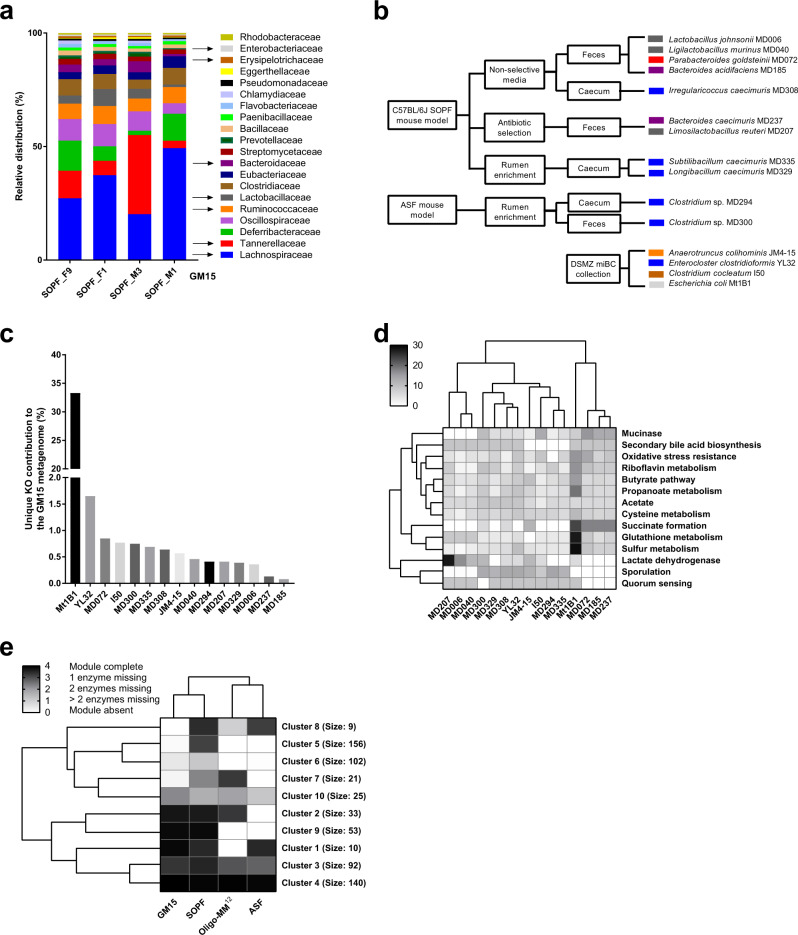
Fig. 1. Selection, isolation, and functional analysis of GM15 strains.
a Representative and prevalent bacterial families identified from fecal samples of 4 C57BL/6J mice of our colony. b Eleven bacterial strains were isolated from fecal or cecal samples of either C57BL/6J or ASF mice using various culture methods. Four additional strains were obtained from the DSMZ collection. c Unique KO (KEGG Orthology) groups are those present in only one GM15 member. The unique contribution of each GM15 member is relatively evenly distributed (<2%), except E. coli whose unique functions contribute for 33%, although nonunique KO groups are primarily responsible for the GM15’s metagenomic profile with 59% of the contribution. d Heatmap of hierarchical clustering of enzymatic activities in the gut for the 15 strains of the GM15 model. In quorum sensing (QS) function, only effector proteins were screened (because receptors suffer from similarities with nonspecific QS receptors). e Heatmap of hierarchical clustering of KEGG module distribution in the metagenomes of GM15, SOPF, ASF, and Oligo-MM12 models. Clusters of KEGG modules are highlighted with their respective size (number of KEGG modules). The list of KEGG modules and clusters is shown in Supplementary Data 1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.