Fig. 4. Schlemm’s canal MIGS devices.
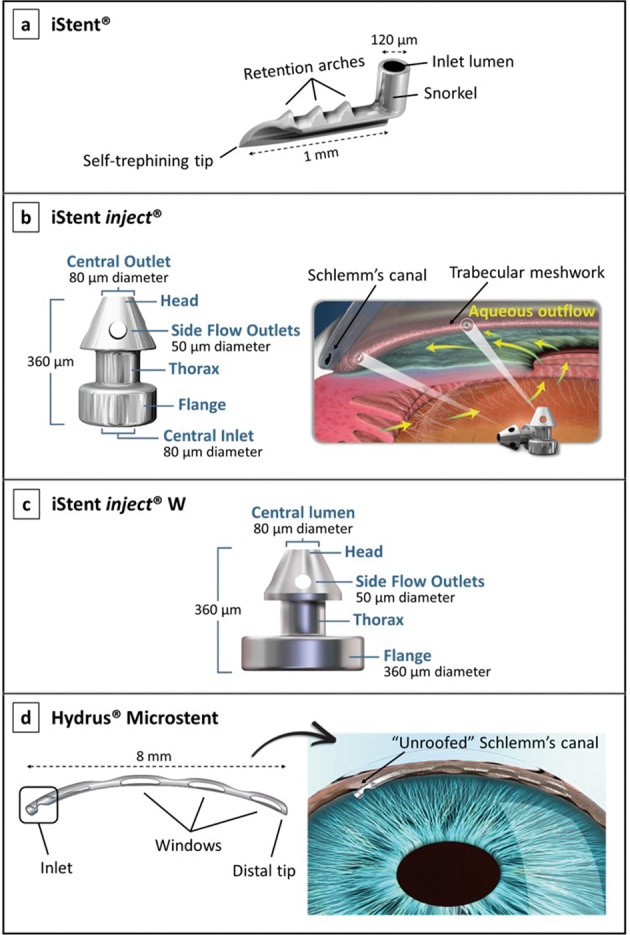
a The first-generation iStent®, showing its self-trephining tip that is inserted into Schlemm’s canal via a sideways sliding technique, its retention arches which help maintaining the device in position, and its lumen that faces the anterior chamber [68]; image courtesy of Glaukos Corporation. b The second-generation iStent inject®, showing its head containing four side ports and designed to fit into Schlemm’s canal, and its flange with an inlet lumen that faces the anterior chamber as illustrated in the figure on the right side [68, 74]; images courtesy of Glaukos Corporation. c The iStent inject® W, showing its larger flange diameter as compared with the previous version iStent inject® [79]; image courtesy of Glaukos Corporation. d The Hydrus® Microstent, showing its three open windows along its anterior surface and its placement in the eye (figure on the right) [75, 76]; images courtesy of Ivantis Inc.
