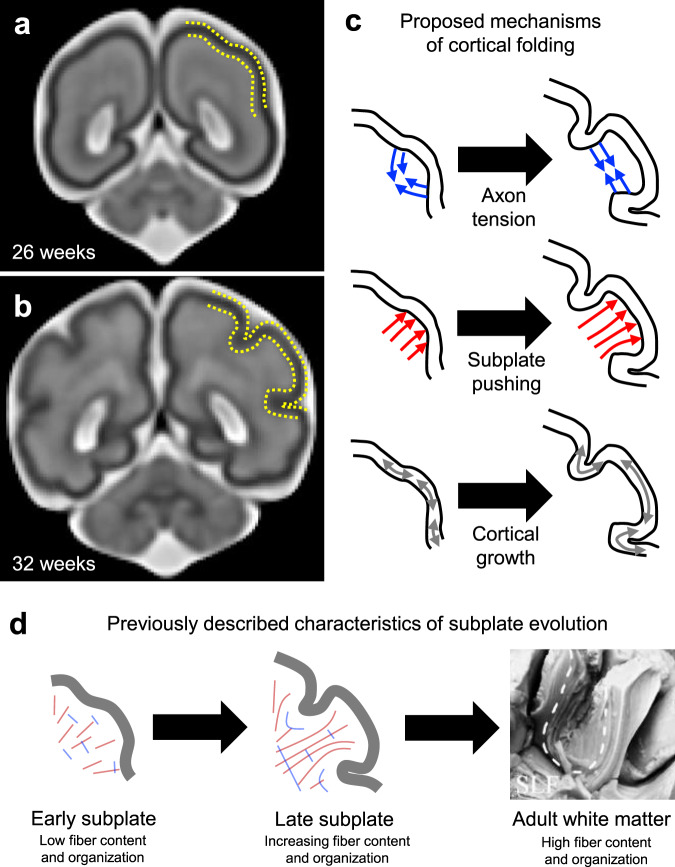
Fig. 1. Cortical folding and subcortical organization.
a–b Magnetic resonance images of the fetal human brain at the onset of cortical folding (a) and after formation of cortical folds (b). Images generated from template described in Gholipour et al.69. c Mechanisms proposed to actively induce cortical folding include axon tension that preferentially tethers specific areas of cortex (top), subplate growth that exerts an outward push to form gyri (middle), and constrained cortical growth, either uniform or patterned, that induces mechanical buckling (bottom). d Schematic illustration of previously reported observations in the developing subplate, including steady increase in axon density during the period of folding and emergence of organization mirroring adult white matter. Image of human brain from Burks et al.41 illustrates predominant organization observed in the adult white matter, including radial organization beneath gyri and tangential organization beneath sulci. Dotted line indicates short association fibers bridging adjacent gyri (U-fibers), SLF = superior longitudinal fasciculus.