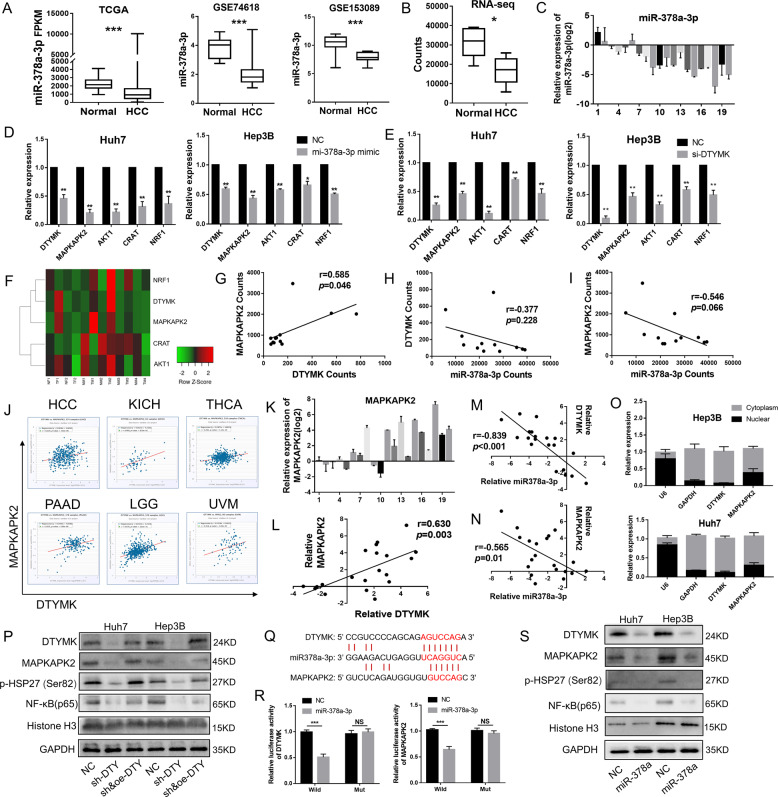
Fig. 3. DTYMK acted as ceRNA to affect the function of MAPKAPK2.
A Decreased expression of miR-378a-3p in HCC from TCGA and GEO. B and C Decreased expression of miR-378a-3p in HCC from RNA-seq of 6 paired HCC tissues and qPCR of 20 paired HCC tissues. D Expression of DTYMK, MAPKAPK2, AKT1, CART, and NRF1 could be inhibited by miR-378a-3p. E Decreased expression of MAPKAPK2, AKT1, CART, and NRF1 after DTYMK knockdown. F Heatmap (RNA-seq) showed a clear correlation between DTYMK and MAPKAPK2. G Positive correlation between DTYMK and MAPKAPK2 (RNA-seq). H and I Opposite relation between miR-378a-3p, DTYMK, and MAPKAPK2 (RNA-seq). J Significant correlation between DTYMK and MAPKAPK2 in multiple cancer types. K and L Increased expression of MAPKAPK2 in 16 of 20 patients with HCC, which correlated with the expression of DTYMK. M An opposite expression trend existed between miR-378a-3p and DTYMK. N An opposite expression trend existed between miR-378a-3p and MAPKAPK2. O Subcellular locations experiments showing that DTYMK and MAPKAPK2 were enriched in the cytoplasm. P Decreased expression of MAPKAPK2 and p-hsp27, and decreased nuclear translocation of NF-κB (p65) after DTYMK knockdown. Q Potential binding sites between DTYMK, MAPKAPK2, and miR-378a-3p. R MiR-378a-3p bound and significantly inhibited the expression of DTYMK and MAPKAPK2. S MiR-378a-3p inhibited the expression of DTYMK, thus inhibiting MAPKAPK2/p-hsp27/NF-κB (p65). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.