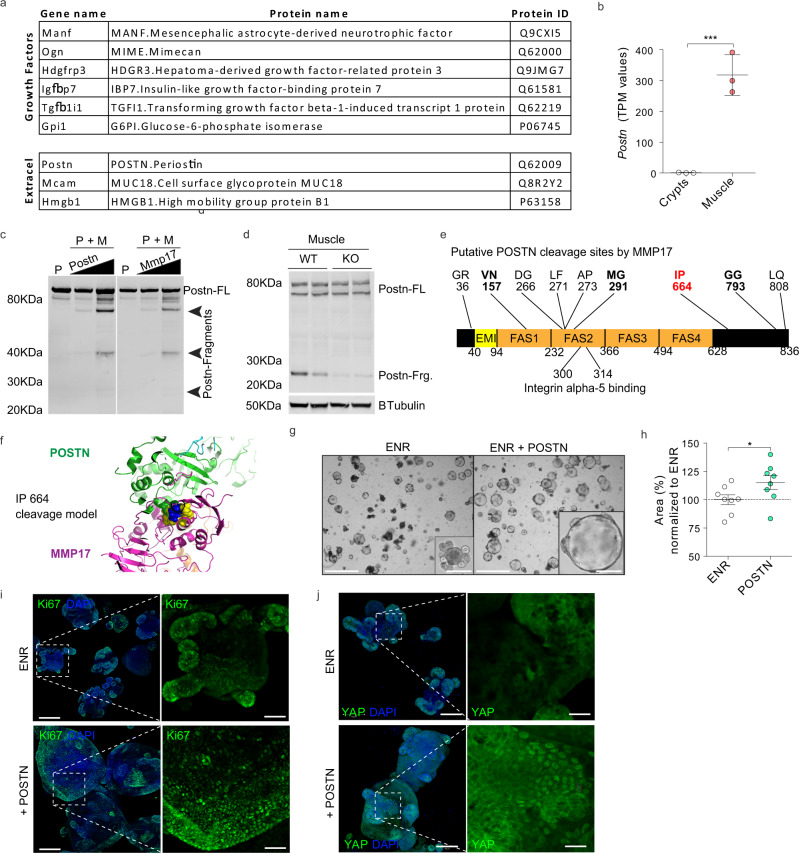
Fig. 8. Identification of smooth muscle-derived factor PERIOSTIN as an in vivo and in vitro substrate for MMP17.
a List of growth factors and extracellular proteins found in muscle-SN. n = 3 biological replicates. b TPM values for Postn comparing crypts with smooth muscle tissue. n = 3 biological replicates. c In vitro digestion experiment with human recombinant proteins showing POSTN fragments when in contact with MMP17 catalytic domain. P, POSTN, M, MMP17, FL, full length. n = 2 experiments with increasing concentrations of POSTN or MMP17. d WB of mouse intestinal muscle showing decreased POSTN fragments in the absence of MMP17. n = 2 biological replicates. e Scheme of POSTN molecule showing putative sites of MMP17 cleavage based on digestion assays followed by MS. Sites that are noted all had 5 or more peptide-spectrum matches (PSMs). In blue and red are available sites after in silico modeling (see Fig. 8f for a model of the best fitted (red) site). f In silico model of MMP17 (magenta)- POSTN (green) docking showing close proximity of 664-665 POSTN cleavage site (cyan) to MMP17 catalytic site (yellow). g, h Representative brightfield images showing SI organoids morphology in the presence of POSTN and area quantification in (h) (Day 3). Scale 1250 and 200 µm in inset. n = 8 wells/genotype pooled from three independently performed experiments with 2–3 wells/experiment. i, j Representative confocal maximum intensity projection images showing YAP or Ki67 (green) staining in POSTN-treated SI organoids. Scale 100 µm; 25 µm in inset (YAP pictures) and 200 µm and 100 µm in Ki67 pictures. Numerical data are means ± SD. Data in (b) represents p-adjusted value from RNAseq analysis (padj value of 1.02e−06), and data in (h) was analyzed by Mann–Whitney test (two-sided, p = 0.0260). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.