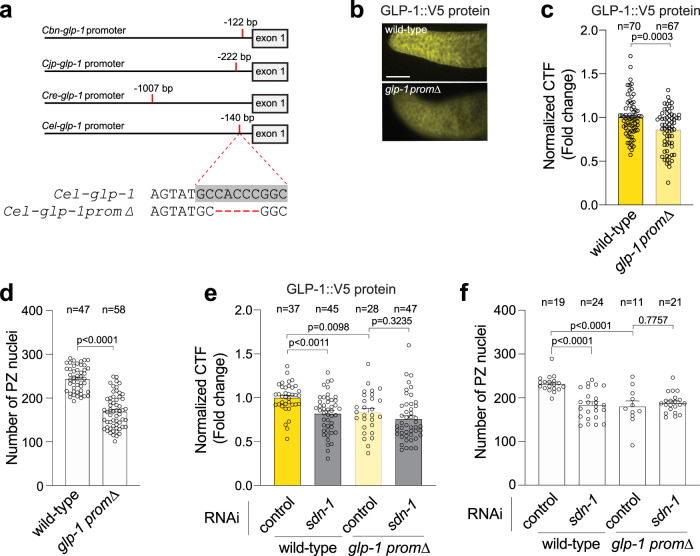
Fig. 3. A conserved promoter motif controls GLP-1 expression and germ cell number.
a Location of a conserved motif in the glp-1 promoter of four Caenorhabditis species. Cbn C. brenneri, Cjp C. japonica, Cre C. remanei, Cel C. elegans. The conserved motif in C. elegans glp-1 promoter is highlighted in gray. Deleted bases in CRISPR-engineered glp-1 promoter mutant in red. b, c Immunofluorescence images (b) and quantification (c) of GLP-1::V5 protein in the distal germline of wild-type and glp-1prom∆ (5 bp deletion in conserved promoter motif) adult hermaphrodites. Data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. and statistical significance was assessed by unpaired t-test. Scale bar = 10 µm. d Quantification of PZ nuclei of wild-type and glp-1prom∆ adult hermaphrodites. Data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. and statistical significance was assessed by a two-tailed unpaired t-test. e Quantification of GLP-1::V5 protein in the distal germline of adult hermaphrodites (± sdn-1 RNAi) expressing wild-type glp-1 or glp-1prom∆ adult hermaphrodites. Data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. and statistical significance was assessed by ordinary one-way ANOVA. f Quantification of PZ nuclei in the distal germline of adult hermaphrodites (± sdn-1 RNAi) expressing wild-type glp-1 or glp-1prom∆. Data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. and statistical significance was assessed by ordinary one-way ANOVA. For all panels, n refers to the number of animals analyzed. P values as indicated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.