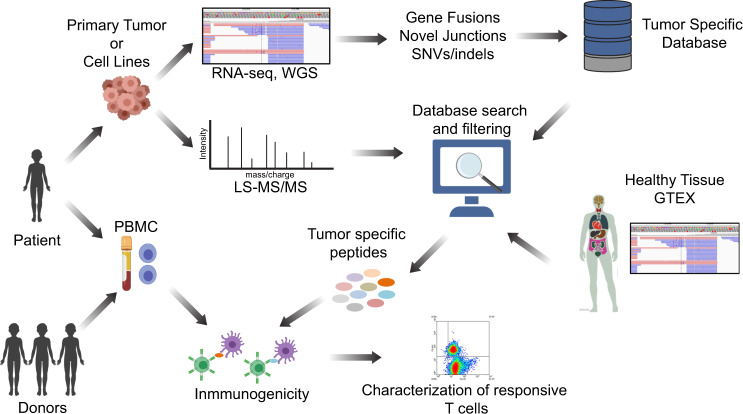
Fig. 1. Proteogenomic approach to identify tumor-specific antigens in pediatric brain tumors.
Schematic representation of the entire workflow is shown. Tumor tissue samples were obtained from patients, and WGS and RNA-seq were performed to identify tumor-specific genomic aberrations (SNV/indels, junctions, and fusions). Protein lysates were subjected to LC-MS/MS shotgun proteomics and spectra were searched against tumor-specific databases originating from tumor WGS and RNA-seq. MS-identified peptides were filtered using genomic and proteomic data from normal tissues to eliminate potential non-annotated normal proteins. Finally, to evaluate tumor-specific peptides for immunogenicity, autologous and allogeneic T cells were selected and expanded against the peptides and characterized for phenotype and function.