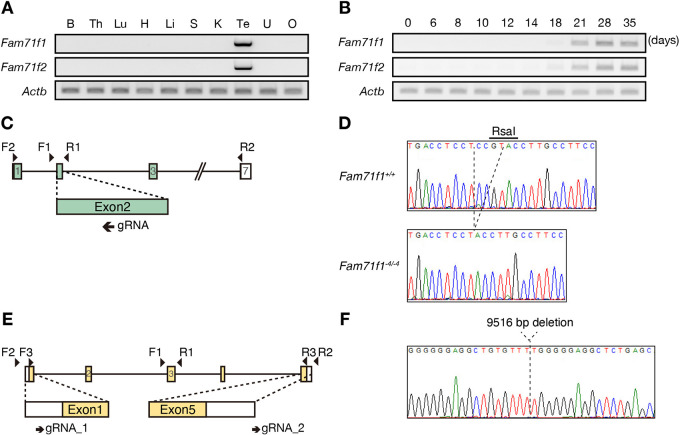
Fig. 1.
Generation of Fam71f1- and Fam71f2-KO mice. (A,B) The expression of mouse Fam71f1 and Fam71f2 was examined by RT-PCR using RNA isolated from various organs (A) and from testis at various postnatal days (B). Both Fam71f1 and Fam71f2 were enriched in testis (A). Strong signals of Fam71f1 and Fam71f2 were detected from postnatal day 21 (B). Actb was used as a loading control. (C) Targeting scheme for generating Fam71f1-KO mice with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The gRNA was designed to target exon 2. Primers F1 and R1 were used for genotyping (Fig. S2A) and F2 and R2 were used for RT-PCR in A,B (Fig. S2B). (D) DNA sequence of Fam71f1 in Fam71f1+/+ and Fam71f1−4/−4 mice. The RsaI recognition site (5′-GTAC-3′) was disrupted by the 4 bp deletion. (E) Targeting scheme for generating Fam71f2-KO mice with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. The gRNAs were designed to target exon 1 and exon 5. Primers F1, F2, R1 and R2 were used for genotyping (Fig. S2D) and F3 and R3 were used for RT-PCR in A,B (Fig. S2E). (F) DNA sequence of Fam71f2-mutant mice. The mutant allele had a 9516 bp deletion. B, brain; H, heart; K, kidney; Li, liver; Lu, lung; O, ovary; S, spleen; Te, testis; Th, thymus; U, uterus.