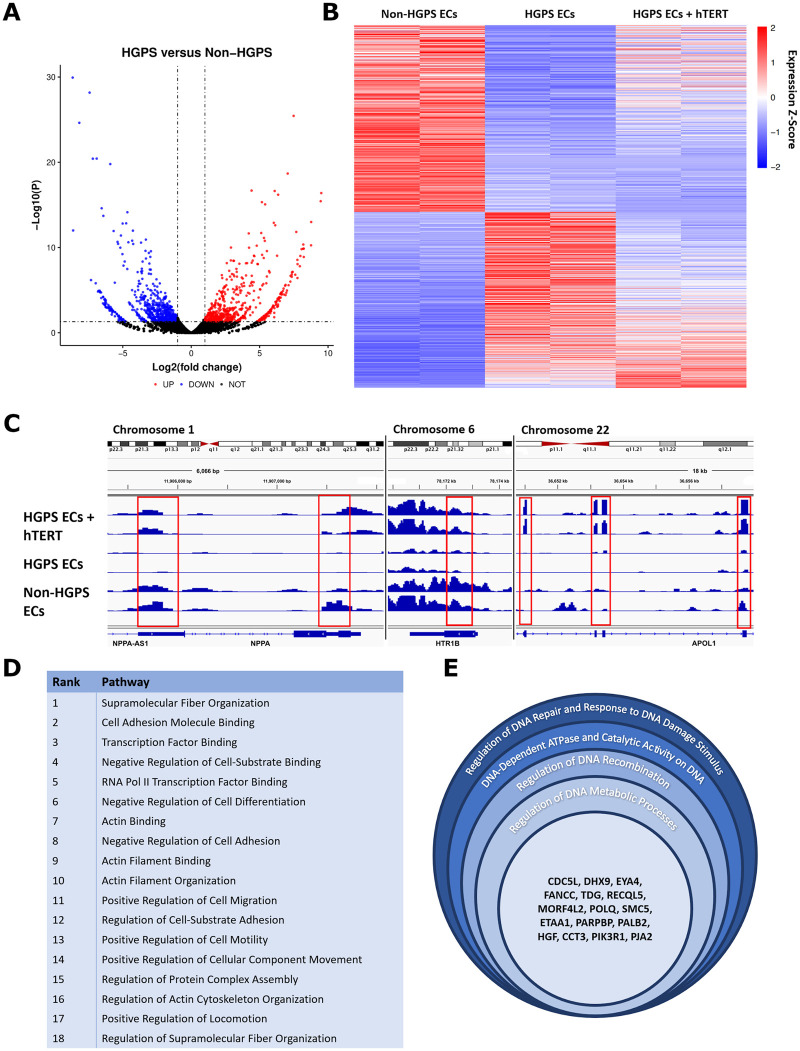
Figure 4.
hTERT treatment rescues global gene expression and endothelial cell pathways in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome endothelial cells. RNASeq analysis uncovered 1285 differentially regulated genes between non-Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome endothelial cells (significance cut-off of P = 0.05 for fold-change ≥1 up or down, A). To further elucidate how hTERT therapy affects global gene expression, genes differentially regulated between non-Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome endothelial cells and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome endothelial cells were then analysed again to assess whether hTERT therapy returned the gene expression to the non-Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome endothelial cell baseline. This analysis is visualized via heatmap in (B) with a significance cut-off of P = 0.05, with example genome browser data showing how the process was conducted for individual, representative genes (C). A total of 256 genes in total were defined as ‘rescued’ via this analysis (see Supplementary material online, Figure S2A), with highly significant pathways identified relating to cellular cytoskeletal organization and motility, DNA damage and repair pathways, and transcription factor binding and regulation. Endothelial cell specific pathways are listed in (D) by rank order significance and (E) shows genes affected related to DNA repair. GO pathways, genes, and the P-values for endothelial specific and non-specific pathways altered by hTERT therapy are detailed in Supplementary material online, Figure S2. Pathway analysis for (D) and (E) were conducted on six biological replicate groups. Non-Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome and Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome endothelial cell lines were differentiated from a parent/child donor set. All the raw sequence data for the samples used in this study are available on the National Center for Biotechnology Information Sequence Read Archive database: Bioproject PRJNA730422.