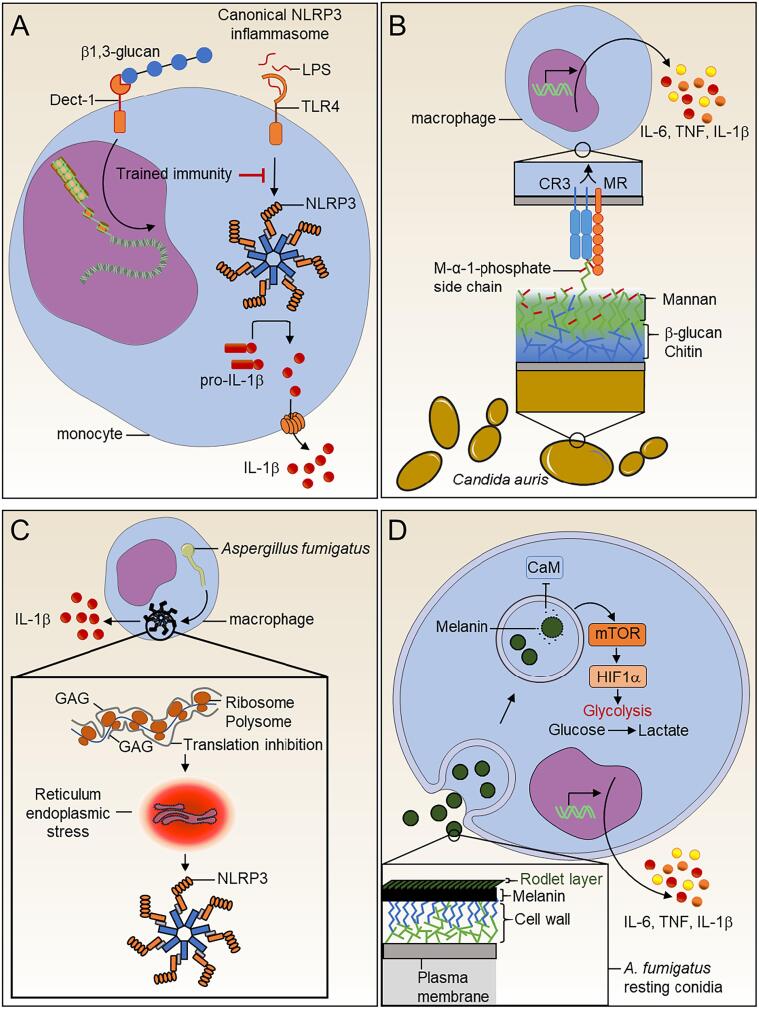
Fig. 1.
Fungal cell wall metabolites modulate our immune system. (A) Fungal β-glucan mediates trained immunity to inhibit canonical NLRP3 inflammasome (B) Host immune system-Candida auris interplay. The C. auris cell surface harbors mannoproteins with specific α-1,2-mannose-phosphate (M-α-1-phosphate) side chains. Macrophage mannose receptor (MMR) and complement receptor 3 (CR3) play a substantial role in the recognition of these specific mannoproteins and the subsequent induction of cytokines. (C)Aspergillus fumigatus galactosaminogalactan (GAG) promotes host immune protection. GAG present at the surface of the germinating conidia directly triggers activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome inside the immune cells. (D) Macrophage metabolism is rewired in response to Aspergillus fumigatus melanin. Fully mature particles of melanin at the surface of the conidia are probably removed during the swelling process, and this inhibits calcium/calmodulin (CaM) signaling in macrophages. Melanin modulation of calcium signaling induces the mTOR pathway, leading to activation of HIF-1α. HIF-1α participates in the transcriptional upregulation of a set of genes for immunometabolic responses. These include not only genes encoding enzymes involved in the glycolysis pathway but also those encoding some pro-inflammatory cytokines.