Figure 2. Centromere specification.
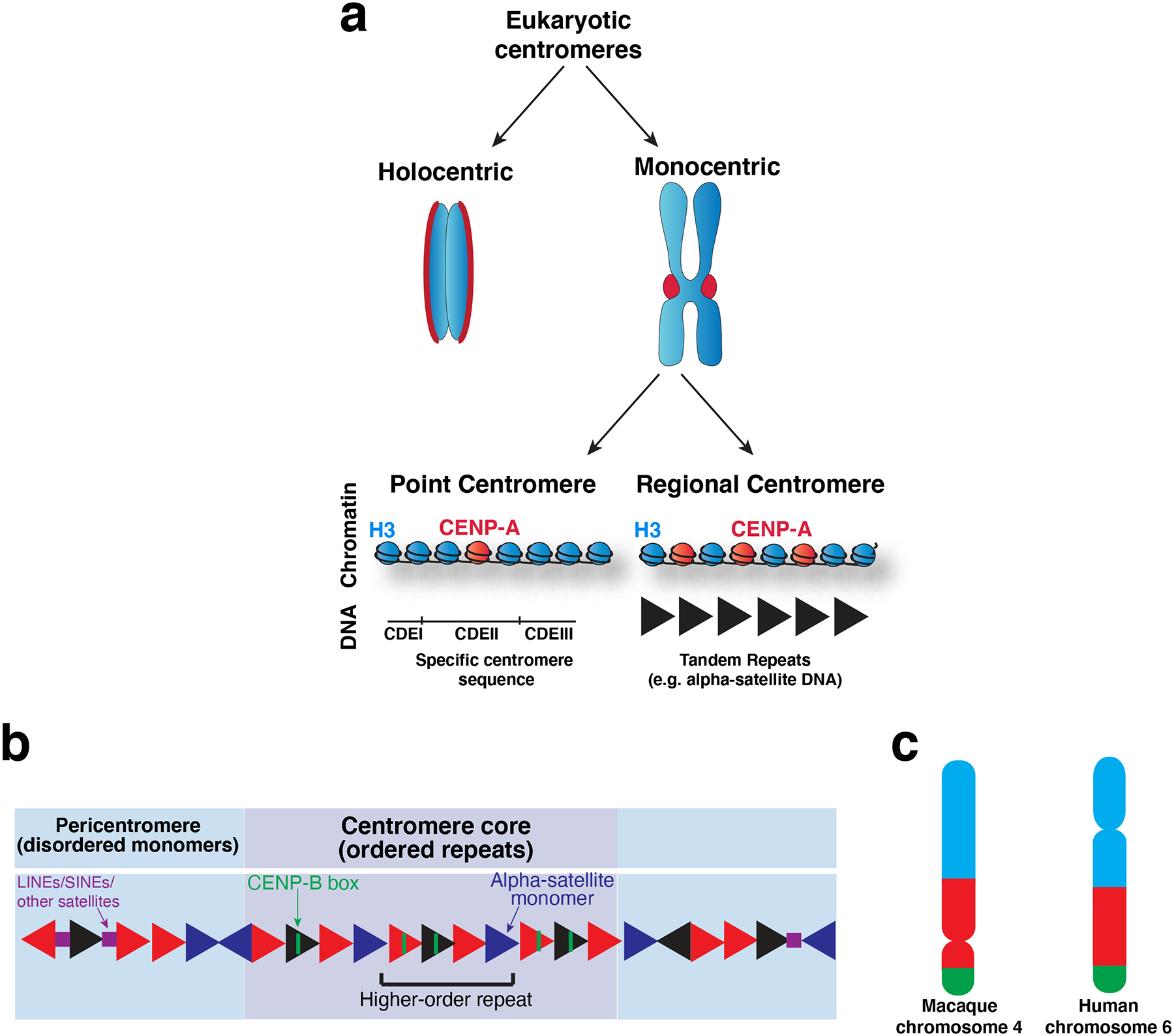
a) Diagram of the diverse types of centromeres found across eukaryotes. Holocentric chromosomes assemble a diffuse centromere across the whole chromosome. Monocentric chromosomes assemble a centromere at a single localized site on the chromosome, which is visible as a constriction between the chromosomes in mitosis (known as the primary constriction). Monocentric chromosomes can be further divided into those with point centromeres and those with regional centromeres. Point centromeres contain a specific DNA sequence that is sufficient for centromere function (here illustrated with the S. cerevisiae DNA architecture), which assembles a single CENP-A nucleosome. Regional centromeres contain large regions of DNA that is often repetitive (such as alpha-satellite DNA in primates), and assemble numerous CENP-A nucleosomes. b) Model of the DNA sequence of primate centromeres. Primate centromeres are built from alpha-satellite monomers (triangles), which are largely but not completely identical, as indicated by the different colored triangles. Patterns of these monomers arranged head-to-tail are re-iterated over the centromere core (purple) as higher-order repeats. Some monomers within the centromere core contain a sequence termed the CENP-B box, which binds to the centromere-DNA binding protein, CENP-B. The centromere core is flanked by less ordered monomers which comprise the pericentromere (blue). LINEs, SINEs and other satellites (squares) are found interspersed with alpha-satellite monomers in the pericentromere214. c) Schematic showing comparison of macaque and human orthologous chromosomes that have undergone centromere repositioning such that the position of the centromere has moved, but the surrounding markers have not, as indicated by the color blocks, which represent syntenic regions. Part c) adapted from33.
