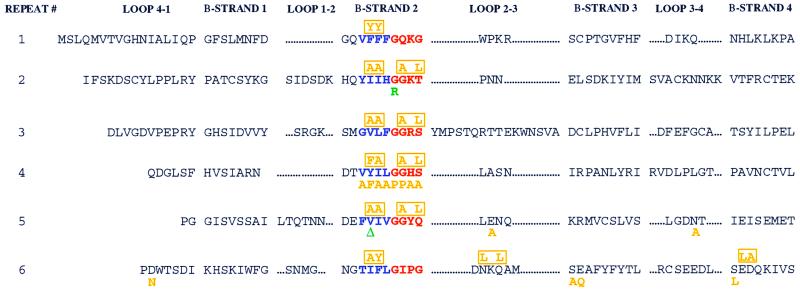
FIG. 1.
Mutations in patients P1 and P2 are localized to the RAG2 kelch repeat domains. Each of the six kelch repeats of the RAG2 active core (13, 40, 41, 52) is formed by four β-strands (1 to 4) separated by loops of variable length (4-1 to 3-4). We present the sequence of mouse RAG2. The second β-strand of each repeat demonstrates the highest level of conservation between various members of the kelch family and is composed of a 4-amino-acid (predominantly hydrophobic) region, displayed in blue. The border of β-strand 2 and loop 2-3 contains a 4-amino-acid glycine-serine-threonine-rich repeat, highlighted in red. Mutations from patients P1 and P2 are noted in green below the affected residue. Note that isoleucine 273 in human RAG2 corresponds to a valine in the mouse sequence. Individual site-directed mutations are displayed in orange below the substituted amino acid, while multiple mutations are indicated and boxed in orange above the altered amino acids.