FIGURE 3.
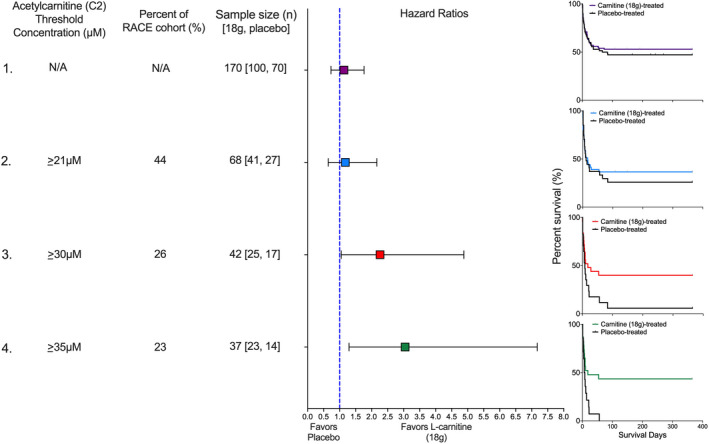
Pretreatment acetylcarnitine (C2) concentration as a predictive clinical trial enrichment strategy. Four scenarios illustrate how different threshold concentrations of acetylcarnitine (C2), a high abundant acylcarnitine would have impacted the outcome of the Rapid Administration of Carnitine (RACE) in Sepsis clinical trial in patients treated with either L‐carnitine (18 g) or placebo. In scenario one, no threshold concentration is used so the entire RACE cohort (n = 236) is eligible. The sample size of 170 patients represents those that received either L‐carnitine (18 g; n = 100) or placebo (n = 70). The hazard ratio is not significant, and consistent with the parent trial, the Kaplan‐Meier curve shows no mortality benefit of L‐carnitine (p = 0.57). In scenario two, an acetylcarnitine (C2) threshold concentration of greater than 21 µM is used. Forty‐four percent (n = 104) of the RACE cohort met this criterion and of these, 68 patients received either L‐carnitine (18 g) or placebo. The hazard ratio is not improved, and the Kaplan‐Meier curve shows no mortality benefit of L‐carnitine (p = 0.59). In scenario three, an acetylcarnitine (C2) threshold concentration of greater than 30 µM is used. Twenty‐seven percent (n = 64) of the RACE cohort met this criterion and of these, 42 patients received either L‐carnitine (18 g) or placebo. The hazard ratio is significant and favors L‐carnitine (18 g); the Kaplan‐Meier curve shows a mortality benefit of L‐carnitine (p = 0.04). Finally, scenario four uses the acetylcarnitine (C2) concentration associated with the maximum Z‐statistic (Table S4), greater than 35 µM. Twenty‐three percent (n = 54) of the RACE cohort met this criterion and of these, 37 patients received either L‐carnitine (18 g) or placebo. The hazard ratio is significant, and the Kaplan‐Meier curve shows a mortality benefit of L‐carnitine (p = 0.01). The number of patients at risk at each time point and the number of censored subjects, which was due to the end of the study (1 year), can be found here: https://doi.org/10.7302/vvqp‐ma61. N/A, not applicable
