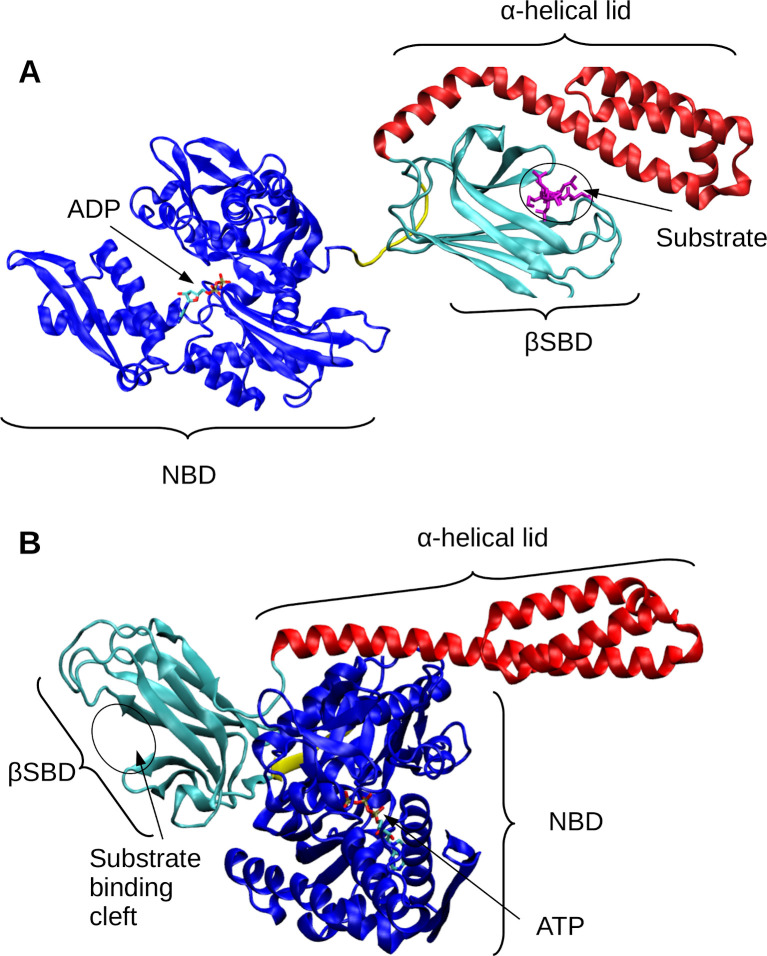
Fig 1. Structural overview of DnaK in substrate-bound and -unbound states.
(A) Structure of DnaK in an unassociated (ADP-bound, substrate bound) conformation (PDB ID: 2KHO [9]). The nucleotide-binding domain (NBD) is shown in blue. The substrate-binding domain (SBD) has two subdomains: the α-helical lid is shown in red, and the βSBD is shown in teal. The substrate from the canonical NR peptide (PDB ID: 1DKZ [10]) is overlaid in the binding cleft of the βSBD in magenta. (B) Structure of DnaK in an associated (ATP-bound, no substrate) conformation (PDB ID: 4B9Q [11]). The ATP molecule is shown based on PDB ID: 3AY9 [12].