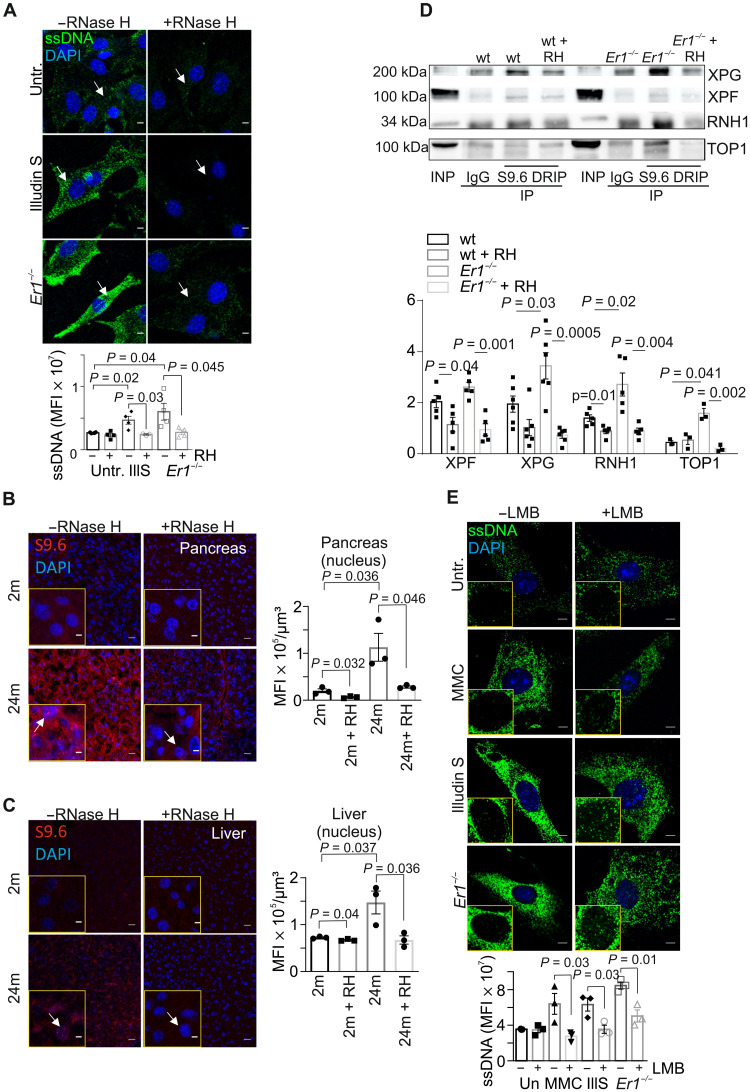
Fig. 5. RPA mediates the nucleocytoplasmic transport of ssDNA moieties.
(A) Immunostaining of ssDNA in Ercc1−/− (Er1−/−) and untreated or Illudin S–treated wt PPCs in the absence or presence of transfected recombinant E. coli RNase H (n = 3 to 4). (B) Immunostaining of R-loops, by means of S9.6 antibody staining, in 2- and 24-month-old naturally aged pancreata in the absence or presence of transfected recombinant RNase H (n = 3). (C) S9.6 immunostaining of R-loops in 2- and 24-month-old livers in the absence or presence of transfected recombinant RNase H (n = 3). (D) S9.6 immunoprecipitation (DRIP) followed by Western blotting for XPG, XPF, RNase H1 (RNH1), and DNA topoisomerase 1 (TOP1) in wt and Er1−/− pancreatic nuclear extracts with and without RNase H (RH) treatment (n = 6). (E) Immunostaining of ssDNA (green) in Er1−/−, untreated, MMC- (10 μg/ml; 4 hours), and Illudin S–treated (30 ng/ml; 3 hours) wt PPCs, cultured with or without the nuclear export inhibitor leptomycin B (LMB; 40 nM). Image inlays show the nuclear ssDNA signal (green) (n = 3). The graphs depict the MFI per cell in (A), per nucleus in (B) and (C), and per cytoplasm in (E). Unless otherwise stated, all tissues and cells are derived from P15 mice. Scale bars, 5 μm. Error bars indicate SEM among n ≥ 3 replicates.