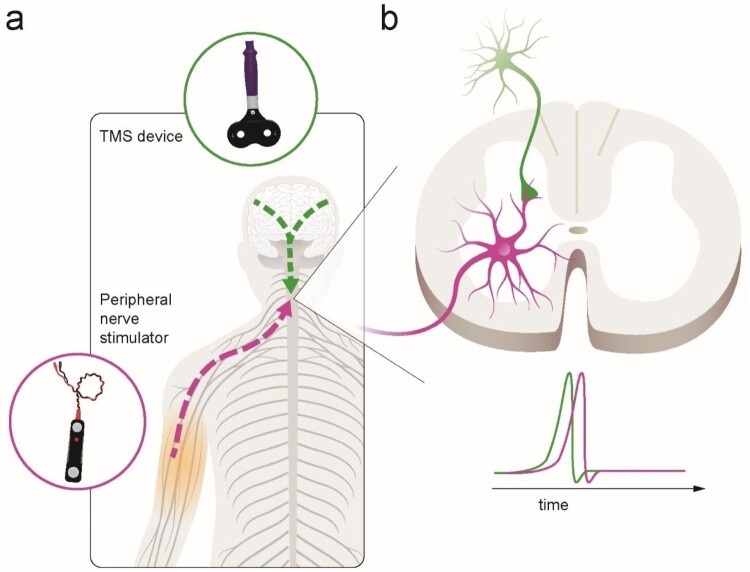
Figure 1.
Illustration of paired corticospinal-motoneuronal stimulation (PMCS). (a). Corticospinal neurons are activated via transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) over each motor cortex (green lines). Spinal motor neurons are activated antidromically via peripheral nerve stimulation (purple line). (b). The interstimulus interval (ISI) between paired pulses allows descending volleys, elicited by TMS, to arrive at the presynaptic terminal of corticospinal neurons (1st, green spike) 1–2 ms before antidromic volleys, elicited by peripheral nerve stimulation, arrive at the dendrites of the corresponding spinal motor neurons (2nd, purple spike). The precise timing is measured for each muscle targeted using central and peripheral conduction times.