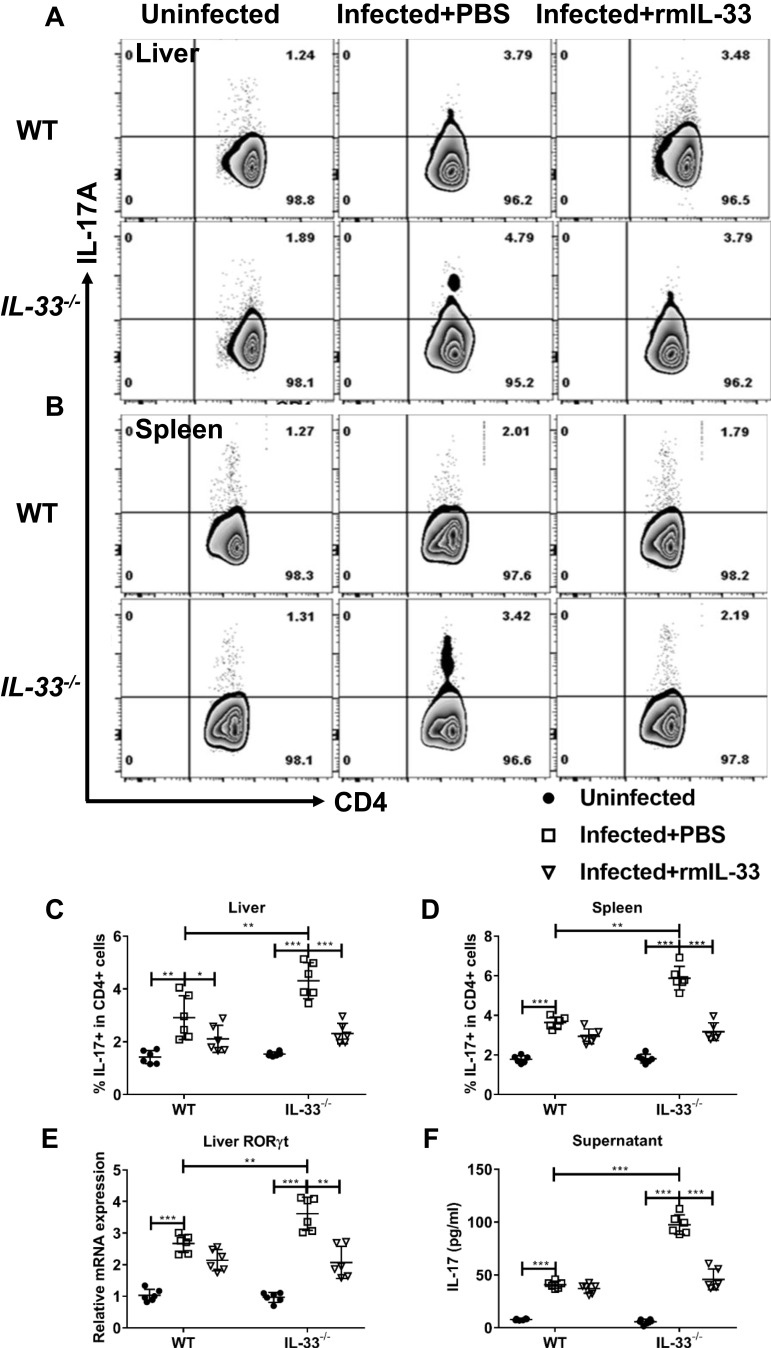
Figure 6.
IL-33 deficiency leads to increased proportion and function of Th17 in murine schistosomiasis japonica. WT and IL-33−/− mice were divided into uninfected group, infected plus rmIL-33 group and infected plus PBS group. Each mouse in the infected groups was infected with 20 cercariae through shaved abdominal skin. Mice in the infected plus rmIL-33 group were intraperitoneally injected with exogenous rmIL-33 (dissolved in sterile PBS solution) from the 4th week to 8th week post infection, with the total 5 μg of rmIL-33 per mouse. The mice in the infection plus PBS group were simultaneously given the equal volume of PBS. At the 8th week post infection, all mice were sacrificed. The liver, spleen and peripheral blood were collected. The proportion of IL-17A+T cells in CD4+ T cells in liver (A and C) and spleen (B and D) of mice. (E) The mRNA expression level of Th17 specific transcription factor RORγt in liver and (F) The concentration of IL-17 in splenic supernatant. Data are expressed as means ± SEMs based on 6 mice in each group and from 2 independent experiments. Asterisks mark significant differences among different groups (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).