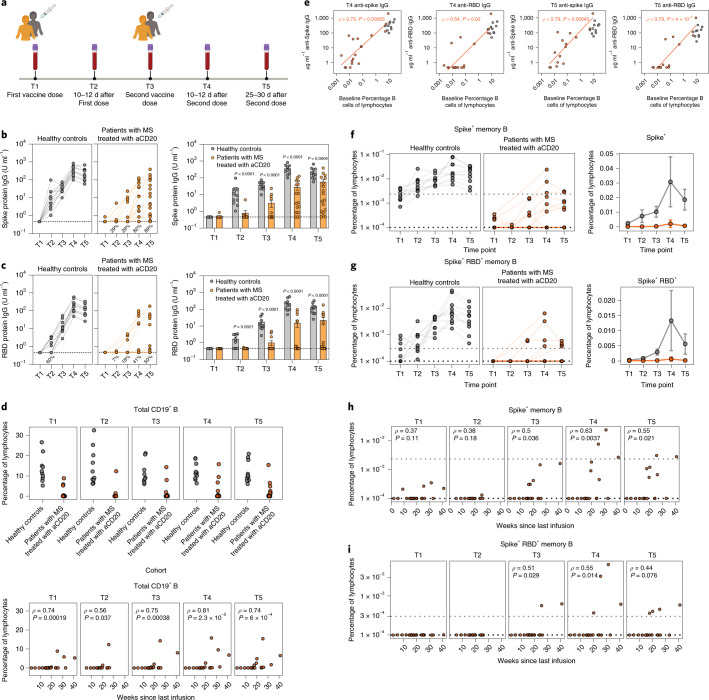
Fig. 1. Decreased humoral responses after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in patients with MS treated with aCD20.
a, Longitudinal study design, vaccine administration scheme and time points collected after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination for healthy controls and patients with MS treated with aCD20. b,c, Anti-spike IgG (b) and anti-RBD IgG (c) for all time points collected (T1–T5) were measured in healthy controls and patients with MS treated with aCD20. Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired, two-tailed, nonparametric Wilcoxon test. The bar plots represent the mean ± s.e.m. d, Top: Frequency of CD19+ B cells as a percentage of total lymphocytes in healthy controls and patients with MS treated with aCD20. Bottom: Correlation between the frequency of total CD19+ B cells and weeks since last aCD20 infusion. Correlations were calculated using nonparametric Spearman rank correlation. e, Correlations between the frequency of baseline (T1) percentage of B cells of all lymphocytes and levels of anti-spike IgG or anti-RBD IgG at T4 (left) and T5 (right) after vaccination. Only patients with MS treated with aCD20 were considered for the correlations, with healthy controls as a visual reference. Associations were calculated using Spearman rank correlation and are shown with Pearson trend lines for visualization. f,g, Frequency of spike+ (f) and spike+RBD+ (g) memory B cells over time in vaccinated individuals. Data are represented as the frequency of antigen-specific cells in the total lymphocyte compartment (left: individual points, log scale; right, mean with 95% CIs, linear scale). h,i, Correlation between the frequency of spike+ (h) and spike+RBD+ (i) memory B cells and weeks since last infusion of aCD20. Correlations were calculated using nonparametric Spearman rank correlation. Gray, healthy controls (n = 10); orange: patients with MS treated with aCD20 (n = 20).