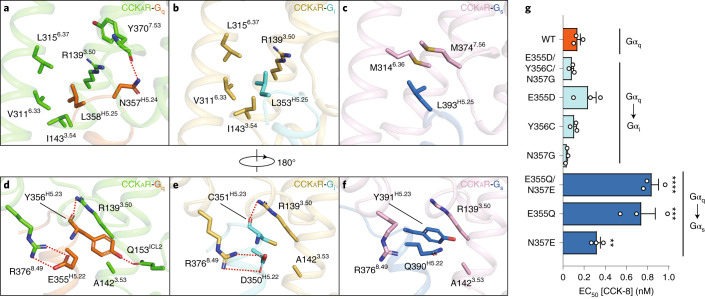
Fig. 4. Distinct interaction patterns of residues from the ‘wavy hook’ motif.
a–c, Details of the interaction between CCKAR and L358H5.25 and N357H5.24 of the Gαq subunit (a), L353H5.25 of the Gαi subunit (b) and L393H5.25 of the Gαs subunit (c). d–f, Details of the interaction between CCKAR and Y356H5.23 and E355H5.22 of the Gαq subunit (d), C351H5.23 and D350H5.22 of the Gαi subunit (e) and Y391H5.23 and Q390H5.22 of the Gαs subunit (f). Hydrogen bonds and salt bridges are indicated as red dashed lines. g, BRET assay evaluating the effects of ‘wavy hook’ substitutions on CCKAR–G protein coupling. The ‘wavy hook’ residues of the Gαq subunit were displaced by the corresponding residues in the Gαs and Gαi subunits. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments (n = 3), conducted in triplicate. All data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance Dunnett multiple comparisons test (P = 1, P = 0.9827, P = 0.7521, P = 0.9994, P = 0.7421, P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001 and P = 0.2078 from top to bottom, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 versus WT).