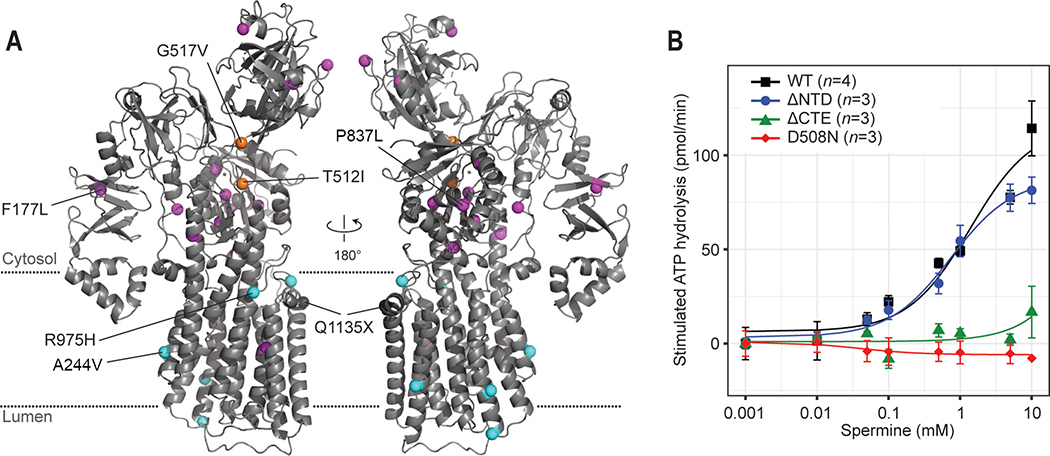
Figure 6. Disease-associated mutations of ATP13A2 and functional importance of CTE.
(A) Positions of disease-associated missense mutations (colored spheres) were mapped onto the ATP13A2 E2P structure. Magenta, mutations that potentially cause protein folding defects. Orange, mutations that potentially alter the D508-phosphorylation reaction (T512I) or P-N interdomain interaction (G517V). Cyan, mutations of unknown mechanisms. Q1135X is also indicated (gray sphere). See also Table S2. (B) Spermine-induced ATPase stimulation of microsomes overexpressing WT ATP13A2 and the ΔNTD, ΔCTE, and D508N (control) mutants (means and s.e.m.). Lines are fitted dose-response curves.