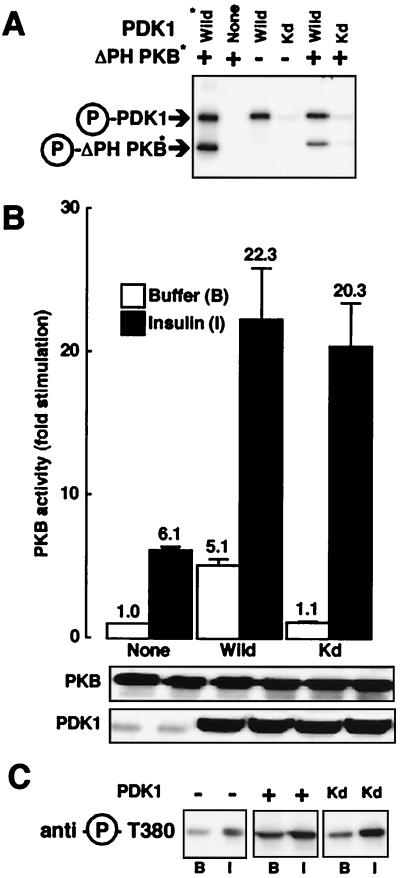
FIG. 2.
Effect of kinase-dead PDK1 on PKB activation. (A) Myc-PDK1 constructs (Wild and Kd) were expressed separately in 293 cells. Immunoprecipitates and PDK1 purified from baculovirus were incubated with [γ-32P]ATP (20 min at 30°C) and ΔPH-PKB purified from baculovirus-expressing Sf9 cells. Samples were subjected to SDS–10% PAGE under reducing conditions followed by autoradiography. Arrows point to the positions of Myc-PDK1, PDK1, and ΔPH-PKB. Asterisks indicate proteins purified from baculovirus-expressing Sf9 cells. (B) 293 cells were transfected with wild-type PKB and, where indicated, with PDK1 constructs. Serum-starved cells were incubated for 5 min in the absence (white bars) or presence (black bars) of insulin (10−6 M). After incubation, cells were lysed, PKB was immunoprecipitated, and its kinase activity was determined using Crosstide as described in Materials and Methods. PKB activity is expressed as fold stimulation compared to basal levels, and the corresponding value is indicated above each column. Values shown are representative of at least four independent experiments performed in triplicate. The levels of the expressed enzymes measured by immunoblotting are shown below the bar graph. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with wild-type PKB and, where indicated, with PDK1 constructs. Serum-starved cells were incubated for 5 min with buffer (B) or insulin (I). After incubation, cells were lysed and 50 μg of the lysates was subjected to SDS-PAGE. PKB phosphorylation was determined by immunoblot analysis with an antibody specifically recognizing phospho-Thr308.