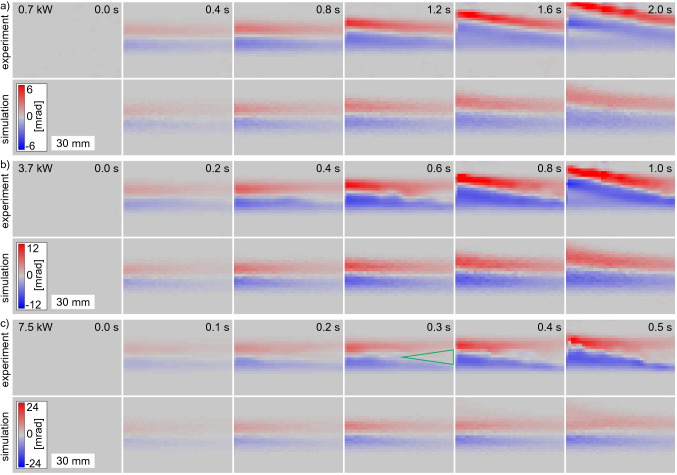
Figure 3.
Differential phase, hence beamlet deflection (positive values represent deflection upwards and vice versa) of horizontal probe beam perpendicular to the high-power laser. Deflection arises due to refractive index changes because of a temperature increase during laser propagation through water. The laser (0.7, 3.7 and 7.5 kW, , continuous wave) is coming from the left. For all input powers an increasing beamlet shift with time and towards the entrance of the water vessel is observed. For 3.7 kW and 7.5 kW, a decreased shift is obtained in the center of the laser path in the back part of the water (green triangle as guide to the eye) due to a significantly decreased energy deposition there because of the thermally induced divergent lens. For 0.7 kW only a homogeneous spot shift increase is observed. After a certain time a convective flow sets in shown here by the upward movement of the area of spot shift. The simulations show a qualitative good agreement with the experimental results.