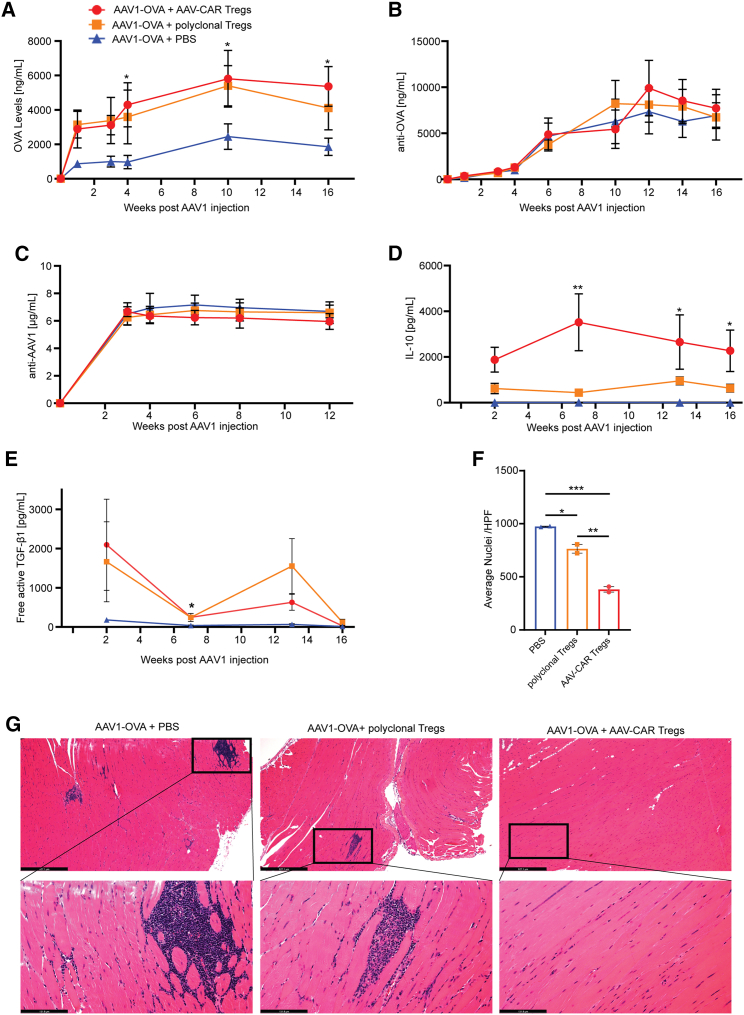
Figure 7.
AAV-CAR Tregs bystander suppress immune response to AAV-delivered transgene
(A) Expression of OVA protein from animals i.m. injected with AAV1-OVA followed by i.v. AAV-CAR Tregs (red), polyclonal Tregs (orange), or PBS (blue) as measured by ELISA. Serum levels of OVA were significantly greater in AAV-CAR Treg-treated animals compared with PBS. (B) Anti-OVA antibodies detected in the serum by ELISA. (C) Anti-AAV1 antibodies in the serum measured by ELISA. (D) Serum levels of IL-10 measured by CBA assay. (E) Serum level of free active TGF-β1 measured by CBA assay over time. Two-way repeated-measure ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons was used (n = 5 for AAV-CAR Treg and polyclonal Treg-treated groups, n = 3 for the PBS treated group for A, B, C, D, and E). (F) Quantification of number of nuclei in i.m. injected muscles. Each dot represents one animal, which is the average of 10 images per animal. (G) Representative images of H&E-stained limb muscles of mice 16 weeks post i.m. injection with AAV1-OVA. Substantial cellular infiltration (blue) was observed in animals treated with PBS or polyclonal Tregs. (Upper) scale bar, 527 μm; (lower) scale bar, 131 μm. one-way ANOVA, n = 2. Error bars are mean ± SEM; ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001. ∗AAV-CAR Tregs compared with PBS.-CAR Tregs compared with PBS.